Cap Protéines Challenge: a 5th edition inspired by oilseeds!
The presentation of the shortlisted projects for the Cap Protéines Challenge 5 took place on December 12. The jury selected six teams to take part in the final on May 19, 2026 in Paris.
La présentation des projets des équipes présélectionnées pour le Cap Protéines Challenge 5 s’est tenue le 12 décembre dernier. Le jury en a retenu six, lesquelles participeront à la finale du 19 mai 2026 à Paris.
Pour cette nouvelle édition, 17 dossiers ont été déposés à l’issue du webinaire de lancement du 18 septembre 2025 avec des projets, lesquels répondent aux thématiques du concours. 8 d’entre eux ont passé la première étape de sélection pour ne laisser plus que 6 concurrents en lice, dont les idées ont séduit le jury d’experts le 12 décembre 2025. La finale se tiendra le 19 mai 2026 à Paris.
Des pommes noisettes à base de féverole

Fevie’s est une équipe d’ingénieurs de Sup’Biotech, qui développe des pommes noisettes à base de purée de féveroles. L’idée est d’introduire un nouvel accompagnement à base de légumineuses, sous une forme familière au sein des familles. Le but est d’en faciliter l’acceptabilité et l’introduction dans les habitudes de consommation.
Innovante, gourmande, rapide à préparer et riche en protéines (11,7g pour 100g de produit), la recette ne contient ni additifs ni conservateurs afin de proposer une recette simple et saine.
Bientôt une plateforme collaborative d’échanges de recettes durables

Cap Veggie est le premier organisme de formation professionnelle en cuisine végétarienne et à base de légumineuses pour la restauration collective et commerciale en grand volume. Aujourd’hui, Cap Veggie dispense des formations, participe à des missions de conseils et de la création de recettes.
Depuis quatre ans, Cap Veggie accompagne plus de mille chefs et équipes de cuisine, une vingtaine d’acteurs de l’agroalimentaire, et régale plus de 2 millions de convives avec ses recettes.
Au 2e semestre 2026, les porteurs du projet lanceront Mijote, la première plateforme web collaborative d’échanges de recettes durables pour les professionnels de la restauration collective.
Du sans gluten à base de protéagineux et oléagineux

Quatre entrepreneuses développent, produisent et commercialisent Floorish. Il s’agit de mixes de farine sans gluten à base de coproduits agroalimentaires revalorisés, issus de filières françaises. Les mixes sont à haute valeur nutritionnelle et enrichis grâce – entre autres – à l’utilisation de protéagineux et d’oléagineux. L’objectif est de réinventer le sans gluten en le rendant plus sain, plus gourmand et plus durable, sans compromis ni sur la texture ni sur le goût.
Les mixes pour pâtisseries et pains sont prêts à l’emploi et peuvent remplacer directement la farine de blé dans les recettes traditionnelles, sans ajustement de formulation.
Un jeu de plateau où l’on cultive des oléoprotéagineux

Cinq étudiants de l’école d’ingénieurs de Purpan propose Proté-Win, un jeu de plateau éducatif où chaque joueur incarne un agriculteur chargé de développer son exploitation en cultivant des oléoprotéagineux. Au fil des saisons, les joueurs doivent faire face aux aléas climatiques, aux maladies, aux fluctuations de marché et aux choix stratégiques de leurs voisins.
Entre négociations, alliances, bluffs et décisions économiques, chacun cherche à optimiser ses cultures, valoriser ses productions et progresser en compétences. Ludique et stratégique, le jeu permet de découvrir de manière simple et immersive les réalités de l’agriculture, la diversité des débouchés et le rôle essentiel des protéines végétales dans la filière.
Du pois chiche dans des plats préparés équilibrés

235 Eat vise à réinventer le prêt-à-cuisiner sec avec des préparations cœur de repas équilibrées, gourmandes et saines Les plus : un peu d’eau et hop, 5 minutes au micro-ondes !
Ce projet est porté par une jeune entrepreneuse passionnée d’innovation et avec l’ambition de lutter contre la malbouffe et le « sautage de repas » ; elle travaille dans des startups de l’agrifoodtech depuis huit ans.
La première gamme de ses prêt-à-cuisiner propose des préparations pour moelleux-repas salés ou sucrés, destinées aux jeunes actifs urbains et dont l’ingrédient clef est la farine de pois chiche. Le lancement est prévu en e-commerce à la fin du premier trimestre 2026.
Des "céréales" croquantes à base de pois chiche

BeanBuddiez est porté par un jeune doctorant à AgroParisTech. Il propose des "céréales" croquantes pour petit-déjeuner ou snack sain fabriquées à partir de pois chiches entiers, 100 % végétales, naturellement riches en protéines, en fibres, sans allergènes et avec une liste d’ingrédients courte. Deux déclinaisons de goûts sont imaginées : un Chico Pop enrobé de miel caramélisé et un Chico Pop à la cannelle.

Building a localized supply chain
Terres Inovia can help you build a new, regionalized industry.
- From strategy to field deployment
- Study of the production potential and economic performance of oilseeds in different production contexts in France.
Notre offre
- Appui stratégique : éclairer les pouvoirs publics et les opérateurs privés sur la faisabilité technico-économique d’une filière oléoprotéagineuse territorialisée grâce à un accompagnement global sur l’ensemble de la chaine de valeur
- Appui sur le terrain : de l’état des lieux jusqu’à l’accompagnement des producteur
- Assemblage de compétences : Mobilisation des meilleurs experts à toutes les phases du projet pour éclairer les décisions
Les grandes étapes
- Etat des lieux
- Expérimentation terrain
- Synthèses et simulations
- Accompagnement au démarrage

These services may be of interest to you
Oilseed impurities
Method used: in-house methodOilseed impurities ISO
Method used: NF EN ISO 658Water content ISO oilseeds
Method used: NF EN ISO 665ISO oilseed cake water content
Method used: ISO 771Would you like a quote?
Would you like to know more about this service or receive a quote? Send us your request!
Fatty acids ISO s/seeds
Method used: NF EN ISO 17059 - NF EN ISO 12966-4

These services may be of interest to you
Building a localized supply chain
Terres Inovia can help you build a new, regionalized industry.From strategy to field…Oilseed impurities
Method used: in-house methodOilseed impurities ISO
Method used: NF EN ISO 658Water content ISO oilseeds
Method used: NF EN ISO 665Would you like a quote?
Would you like to know more about this service or receive a quote? Send us your request!
Agronomic control of chickpea and lentil cultivation in the southwest of France
Our other training courses
Integrating lentils and chickpeas into your crop rotations: a strategic agronomic choice
Lentils and chickpeas are economical, high-performance crops that improve soil fertility, break pest and disease cycles and offer secure outlets. Adapted to the pedoclimatic context of the South-West of France, the training course offers theoretical contributions and visits to master technical itineraries and integrate these legumes in a sustainable way.
Program:
1 Introduction to legumes:
- Definition of legumes and how they work,
- Role of legumes in soil fertilization and crop rotation.
2 - Lentil management in the South-West of France
- Agronomic characteristics: spring species, low-input crop
- Typologies (blond, coral, green) and value-adding opportunities
- Adapting the technical itinerary to regional constraints: soil types, water availability, temperatures, etc.
- Planting, varietal selection, cultural management, fertilization, protection
- Harvesting: optimal conditions, equipment settings
3. chickpea management in south-west France
- Agronomic, environmental and economic benefits
- Regionalized technical itinerary: choice of sowing dates, densities, management in dry conditions, harvesting, storage and contracting.
- Management of pests and diseases specific to the region
4 Focus on organic farming
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Explain the agronomic functioning of lentil and chickpea crops
- Identify their agronomic, economic and environmental benefits
- Choose species and varieties suited to the soil and climate conditions of the South West of France
- Implement rational crop management: planting, fertilization, weed and pest management
- Diagnose the main crop accidents
- Apply good harvesting and post-harvest practices
- Integrate the specificities of organic farming into the local context
Face-to-face format:
-
In-class technical input: presentations, case studies, interactive discussions
-
Practical application in the field: plot visits, crop observation, etc.
Active methods: Illustrated presentations, debates, questions and answers, feedback
Evaluation: Quizzes, questions and answers, application exercises, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment
Theoretical support: Lectures, visual presentations, written material given to participants.
Field visits: Analysis of lentil and chickpea crops in real-life conditions, identification of key technical points.
Practical exchanges: Feedback from field experience and group discussions with the trainer.
Advisors/Technicians from development, economic and agri-supply organizations. Teachers. Farmers Quiz, Q&A, application exercise, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioningIf you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: c.caro@terresinovia.fr
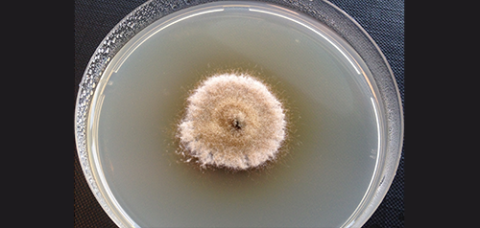
Aucun 480€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/lbtwyvkbn8bvqvbt4nyx2slplj6xg7zlk8vvm56Aknkx47tzmzcdm9shmA7f1ndcl2zt1pj5hjz2yvd3388238ldn8zwszktg8ctq9jrgbfAcpj8 1 Jour Quentin LAMBERT 94 Inter-company and intra-companyFungal strain on culture medium
Supply of mycelial growth on culture medium for the fungal species described below.
Price: from 107€ excl. tax per strain
Alternaria brassicae, Alternaria brassicicola, Alternaria tenuissima, Aphanomyces euteiches, Aphanomyces cochlioides, Ascochyta pisi, Ascochyta fabae, Ascochyta rabiei, Botrytis cinerea, Botrytis fabae, Cladosporium sp, Cylindrosporium concentricum, Colletotrichum lini, Colletotrichum lupini, Epicoccum sp., Fusarium oxysporum, Fusarium solani, Leptosphaeria maculans, Leptosphaeria biglobosa, Leptosphaeria lindquistii, Macrophomina phaseolina, Penicillium sp., Phomopsis helianthi, Phoma medicaginis, Phomopsis phaseolorum, Rhizoctonia sp., Pythium sp., Pseudomonas syringae pv. pisi, Rhizopus sp., Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Sclerotinia trifoliorum, Septoria linicola, Septoria glycines, Stemphyllium sp., Trichoderma sp., Verticillium dahliae, Verticillium longisporum.
These services may be of interest to you
Building a localized supply chain
Terres Inovia can help you build a new, regionalized industry.From strategy to field…Oilseed impurities
Method used: in-house methodOilseed impurities ISO
Method used: NF EN ISO 658Water content ISO oilseeds
Method used: NF EN ISO 665Would you like a quote?
Would you like to know more about this service or receive a quote? Send us your request!
Pathological diagnosis on plant material
Diagnosis by macroscopic and microscopic observation, supplemented if necessary by molecular analysis and/or isolation of the pathogenic micro-organism on culture medium. The results are transmitted in the form of a report.
Price: from €268 excluding VAT

These services may be of interest to you
Building a localized supply chain
Terres Inovia can help you build a new, regionalized industry.From strategy to field…Oilseed impurities
Method used: in-house methodOilseed impurities ISO
Method used: NF EN ISO 658Water content ISO oilseeds
Method used: NF EN ISO 665Would you like a quote?
Would you like to know more about this service or receive a quote? Send us your request!
Optimization of crushing and mechanical extraction of oil-protein seeds
Our other training courses

Training catalog
Discover all the field crop training courses offered by Arvalis and Terres Inovia.
Deepen your understanding of crushing processes and the mechanical extraction of oil-protein seeds.
This course will enable you to analyze in detail the impact of process parameters on the chemical composition of oils (fatty acids, phospholipids, undesirables) and on the nutritional quality of oilcakes (digestibility, anti-nutritional factors). It incorporates the latest advances in mechanical extraction and proposes an applied approach to optimize de-oiling performance and meet the technical requirements of industrial sectors.
Program:
Day 1: Fundamentals and practices of mechanical oilseed extraction
- Oil chemistry: fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, sterols and phytosterols, waxes. Properties, risks of deterioration
- General information on seeds & hulling with a focus on sunflower: hulling, variability of oil quality linked to growing conditions and varieties.
- Extraction mechanics: compression, filtration, viscosity, press geometry
- Workshop visit: press study, analysis tools, case studies
- Feedback & case studies
Day 2: Heat treatment, product quality and industrial optimization
- Mechanics of baking
- Importance of baking
- Heat treatments & Oil and cake quality
- Feedback & case studies
- Process optimization tools
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Identify the main chemical and nutritional characteristics of oils derived from oilseeds
- Analyze the effects of crushing processes on oil and cake quality
- Explain the operation of mechanical extraction processes and their critical parameters
- Assess the suitability of processed products for end-users (animal nutrition, industry)
- Use numerical tools to simulate, predict and optimize production performance
Theoretical and technical input: detailed presentations of the fundamentals (oil chemistry, extraction mechanisms, critical parameters), illustrated by diagrams and scientific data.
Case studies and feedback: analysis of real industrial situations, sharing of best practices and discussion of solutions.
Hands-on workshop visit: observe equipment (presses, analysis tools), demonstrate processes, manipulate parameters and analyze results in real time.
Interactive exchanges: question-and-answer sessions, quizzes to validate acquired knowledge, debates between participants and trainer.
Presentation aids given to participants: paper or digital documents: presentations, diagrams, key data, bibliography.
Digital optimization tools : use of software (Excel, solver) to simulate and optimize processes.
Case studies: role-playing on industrial problems, collective analysis of solutions.
Workshop visit: possibility of a half-day workshop visit to see the effects of controllable parameters on de-oiling performance.
Technical managers, crushing plant operators or managers, agro-industrial processing professionals, R&D engineers, process technicians. End-of-session quiz, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioningIf you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: c.caro@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 960€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/nfmw5s6jnrqvs7jpmjhhk8bpgy7v19cnlj6h3sl2pft2wssf4rdvsrs5j8mwyAlr4rngwpj5hj52qztgg88g5At3k8sAAmsd3nsd3sdg4vyw4pj8 2 Jours Patrick CARRE 48 Inter-company and intra-companyHerbi1&NoPhy
OFB
1 200 000€
60 months Oui NationalThe challenges
Herbicide management is at the heart of farmers' concerns. There is a strong need for references in a context where the number of active ingredients is decreasing, resistance is developing and climate change is having an impact on weed dynamics and intervention times.
Following on from the XpeGE 0 project, which tested systems without phytosanitary products, Herbi1&NoPhy is based on less risk-taking for farmers and supply chains: the use of herbicides is a low priority, well after agronomic levers - but not excluded - and the use of other phytosanitary products is circumvented by technical choices.
The evaluation of this new project should make it possible to measure the technical and economic consequences of very drastically reducing the use of phytosanitary products, with a view to adapting systems to climate change, based on the notion of diversity (species, varieties, tillage, sowing periods, etc.).
The objectives
The aim of this experimentation and transfer project is to consolidate, build up and disseminate references on field crop and mixed farming systems, with a marked break in the use of phytosanitary products adapted to the context of climate change. It is based on a strong technical partnership between research, development, teaching and farmers.
The experimental sites (2 platforms and 10 observatories) will test annual cropping systems that represent a major break with the past, using all available agronomic, genetic, mechanical and biocontrol levers, with minimal use of herbicides and the use of other products only when absolutely necessary.
Expected results
The aim of the project is to create benchmarks for low-use phytosanitary practices. Estimating the technico-economic impact, the consequences in terms of equipment investment or working time, and assessing the acceptability of these systems to farmers through controlled observatories are the results expected from the project to help farmers adopt these systems.
The role of Terres Inovia
Partner
- Technical intervention on the Haroué platform
- Reflection on intervention thresholds as a last resort
Do you have a question?
Contact our specialist who will respond promptly to your request.
These projects may be of interest to you
Here are some other projects dealing with the same themes.
PLATOON
Towards better management of the cruciferous clubroot problem (Plasmodiophora brassicae): from knowledge of the pathogen to varietal evaluation
Decoproze
Demonstrator of a sustainable, zero-emission, protein-rich rapeseed production chain
ARPEGE
Structuring and developing sustainable agricultural sectors with regenerative agriculture
Project sheet
Towards carbon neutrality with farms
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Sed non risus. Suspendisse lectus tortor, dignissim sit amet, adipiscing nec, ultricies sed, dolor. Cras elementum ultrices diam. Maecenas ligula massa, varius a, semper congue, euismod non, mi. Proin porttitor, orci nec nonummy molestie,…Aurore Baillet - a.baillet@terresinovia.fr
01 janvier 2025 S'adapter au changement climatique Grand Est Regional Chamber of Agriculture En cours NonClieNFarms
GreenDeal Europe
13,500,000€ (of which €1,200,000 funded by the EU)
48 months Oui EuropéenThe challenges
In support of the Green Deal for Europe, the project aims to innovate and engage stakeholders in the agricultural world to support the transition of agriculture and strengthen efforts to mitigate climate change. To reduce greenhouse gas emissions by at least 50% by 2050 and increase carbon sequestration in agricultural soils, a strong systemic approach is needed. The challenge is to develop, co-design and scale up systemic and locally relevant solutions to promote climate-neutral and resilient European agriculture.
The project is coordinated by INRAE and brings together 33 partners, including Acta (representing Terres Inovia, Institut de l'élevage and Arvalis) and private companies (Nestlé, Danone and EDF).
The objectives
ClieNFarms is a European project that aims to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from the agricultural sector, starting from the farm scale and crossing it with the sector and territory scales. The aim is to achieve a GHG reduction of at least 50% by 2050, so that the agricultural sector can contribute to achieving carbon neutrality in the region (i.e., not emitting more emissions into the air than can be offset by sequestration via forests, agricultural soils or other means).
The project supports farmers in their efforts to reduce emissions and store more carbon in the soil to offset residual emissions as far as possible.
Expected results
- Setting up stakeholder dynamics in territorial case studies
Innovative systemic solutions for climate change mitigation are tested in some twenty territorial case studies across Europe (including 5 in France, with 2 in field crop systems), and assessed using modeling approaches and multi-criteria evaluations.
These territorial case studies (christened I3S for "innovative systemic solution space") will cover the diversity of production systems (crops, livestock, dairy products, special crops, etc.) and geographical situations (from East to West and North to South Europe, as well as New Zealand).
Each territorial case is then organized around a demonstration farm for more precise measurements, around 10 pilot farms to implement mitigation levers in agricultural situations, and around 100 neighboring farms to raise awareness through information dissemination actions (visits, surveys, documents).
On this basis, a "creative arena" of the territorial case aims to bring together other players in the area's sector in order to accelerate and facilitate farmers' efforts.
- Exchanging knowledge and references on mitigation levers and support tools
- Avenues for scaling up mitigation efforts, for massification on a territorial or sectoral scale, or for facilitating carbon markets.
- Messages to, and exchanges with, other R&D groups or national or European policy bodies on the subject of mitigation.
The role of Terres Inovia
Partner
In the ClieNFarms project, Terres Inovia is represented by Acta. The Institute is coordinating a territorial case study (I3S) in northeastern France for field crops, which includes the territorial massification study. It contributes to inter-country coordination on mitigation levers for the field crop sector, and participates in communication and networking initiatives.
Achievements and spin-offs
Do you have a question?
Contact our specialist who will respond promptly to your request.
Our partners
- INRAE
- Agacal
- Agrisearch Limited
- Agricircle AG
- ACTA
- Berner Fachhochshule
- Bioforum
- BioSense Institute
- Center wallon de Recherches agronomiques
- Climate Kic holding BV
- CEA
- CONSULAI
- Dantrade BV
- ENSFEA
- EDF
- FC CV
- FiBL
- GWCT
- IBNA
- IFOAM Organics Europe
- JLU
- Massey University
- Nestlé France
- Nestlé UK Ltd
- Nestle Ukraine LLC
- Nestlé Suisse SA
- Nutrifarms
- Stichting Wageningen Research
- Teagasc
- The University Court of the University of Aberdeen
- Universita Cattolica del Sacro Cuore
- University of Leeds
These projects may be of interest to you
Here are some other projects dealing with the same themes.
PLATOON
Towards better management of the cruciferous clubroot problem (Plasmodiophora brassicae): from knowledge of the pathogen to varietal evaluation
-
Colza
Tournesol
Pois de printemps
Pois d'hiver
Pois chiche
Lentille
Soja
Chanvre
Féverole d'hiver
Féverole de printemps
Lin d'hiver
Lin de printemps
Lupin d'hiver
Lupin de printemps
Cameline
Biodiversité
Herbi1&NoPhy
Experimenting with agroecological systems for pesticide use as a last resort
Decoproze
Demonstrator of a sustainable, zero-emission, protein-rich rapeseed production chain
ARPEGE
Structuring and developing sustainable agricultural sectors with regenerative agriculture
Anne Schneider a.schneider@terresinovia.fr
01 janvier 2022 Renforcer la souveraineté en huiles et protéines INRAE En coursChickpeas
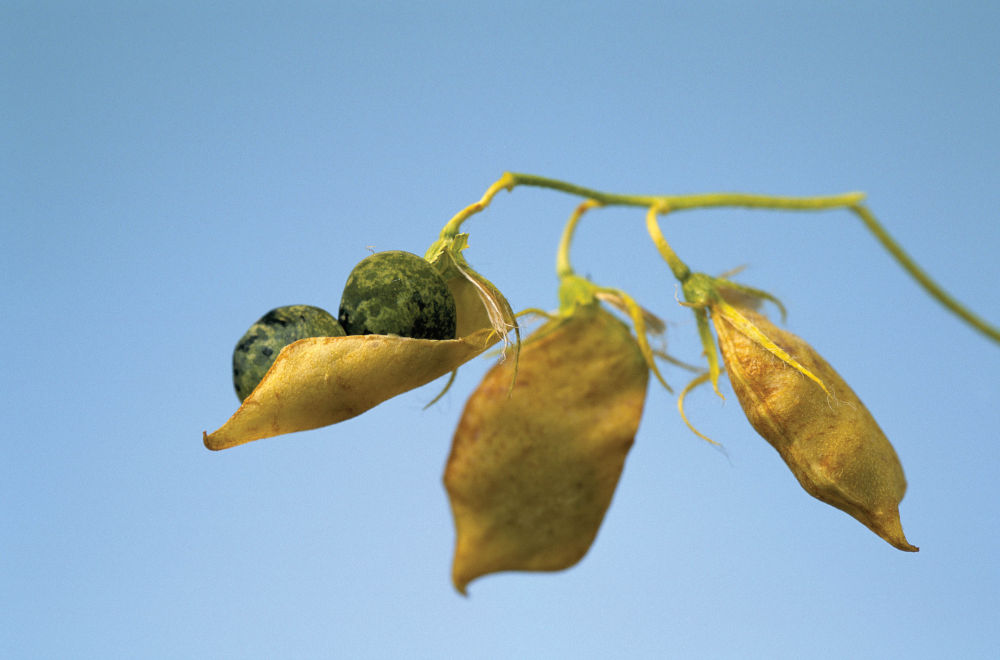
Rich in protein, chickpeas are used exclusively for human consumption. Sown between mid-December and mid-April and harvested between early July and late August, the crop is adapted to the Mediterranean climate and can withstand relatively high water stress. Like all seed legumes, chickpea is capable of fixing atmospheric nitrogen (if combined with its specific rhizobium) and requires no nitrogen fertilizer.

Projects
Every year, Terres Inovia participates in or coordinates several national, European and international calls for projects on various themes.
-
Colza
Tournesol
Pois de printemps
Pois d'hiver
Pois chiche
Lentille
Soja
Chanvre
Féverole d'hiver
Féverole de printemps
Lin d'hiver
Lin de printemps
Lupin d'hiver
Lupin de printemps
Cameline
Biodiversité
Herbi1&NoPhy
Experimenting with agroecological systems for pesticide use as a last resort
Project sheet
Towards carbon neutrality with farms
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Sed non risus. Suspendisse lectus tortor, dignissim sit amet, adipiscing nec, ultricies sed, dolor. Cras elementum ultrices diam. Maecenas ligula massa, varius a, semper congue, euismod non, mi. Proin porttitor, orci nec nonummy molestie,…Events
The next chickpea events we are organizing
-
Colza
Tournesol
Pois chiche
Lin d'hiver
Lin de printemps
Pois d'hiver
Pois de printemps
Lentille
Soja
Chanvre
Féverole d'hiver
Féverole de printemps
Lupin d'hiver
Lupin de printemps
Cameline
Maladies
Cultural assets
Diversifier son système de culture
Gérer son système de culture
Terres Inovia Technical Meeting 2026 - Blois (41)
-
Colza
Tournesol
Lin d'hiver
Lin de printemps
Pois d'hiver
Pois de printemps
Féverole d'hiver
Féverole de printemps
Lupin d'hiver
Lupin de printemps
Pois chiche
Maladies
Cultural assets
Diversifier son système de culture
Gérer son système de culture
Terres Inovia Technical Meeting 2026 - Central and Western Zone - Cloned
-
Pois d'hiver
Pois de printemps
Pois chiche
Lentille
Soja
Féverole de printemps
Féverole d'hiver
Lupin d'hiver
Lupin de printemps
Cap Protéines Challenge 5
Training
Develop your skills with camelina training courses designed and run by Terres Inovia experts.
Editions
Terres Inovia can provide you with several technical publications on chickpeas.
Services
Fatty acids ISO s/seeds
Method used: NF EN ISO 17059 - NF EN ISO 12966-4Fungal strain on culture medium
Supply of mycelial growth on culture medium for the fungal species described below.Price: from…Pathological diagnosis on plant material
Diagnosis by macroscopic and microscopic observation, supplemented if necessary by molecular…Weeds: characterization of sensitivity to ALS inhibitors
Research by molecular analysis (sequencing) of mutations in the acetolactate synthase gene…Have a question? Please contact us!
If you have any questions or thoughts about our research, initiatives or projects, please don't hesitate to write to us.
Log in to contact your regional contact
If you do not wish to create an account, please use the contact form.
Key figures
hectares
Benefits
Adapted to climate change
Chickpea is adapted to the Mediterranean climate and can withstand relatively high water stress.
A short cycle
Chickpea is a short-cycle crop, lasting between 6 and 7 months from sowing to harvest.
Excellent precedent
Chickpea is capable of fixing atmospheric nitrogen, enabling the following crop to benefit from it.
Growing guide
This comprehensive guide is divided into chapters covering everything you need to know about growing chickpeas: seeds, choosing the right plot, planting, inoculation, fertilization, weeding, harvesting and storage. It highlights the advantages of growing chickpeas and explains how to control the pests and diseases that affect them.












