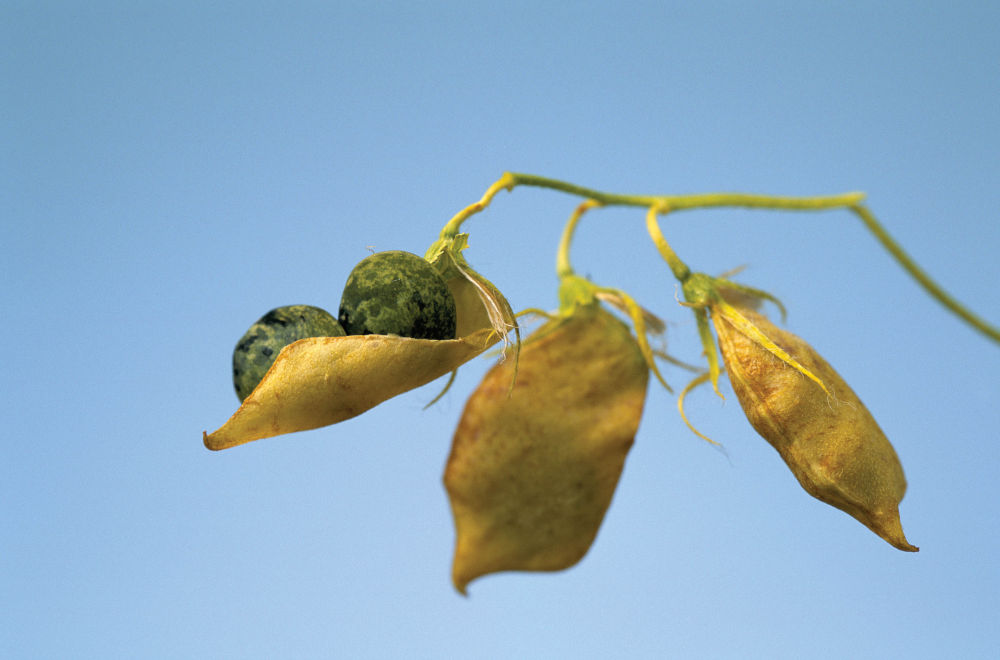
Diagnosing and managing pea and faba bean diseases
Our other training courses
Anticipate, identify, act: faced with the challenges of sustainable agriculture, controlling pea and faba bean diseases is becoming a key lever. Thanks to this practical, targeted training course, you'll learn how to effectively recognize symptoms, understand epidemiological mechanisms and implement the best management strategies. A day to gain expertise, secure your crops and implement integrated protection in your practices.
Program:
Disease identification:
- Presentation of symptoms of common pea and faba bean diseases using visual aids (photographic documents and samples of diseased plants).
- Study of airborne and root diseases
Epidemiological knowledge:
- Understanding pathogen life cycles
- Climatic and cultural conditions conducive to disease development
- Epidemic dynamics (sources of inoculum, period of contamination, survival of pathogens in the soil or on residues)
- Influence of agricultural practices (rotation, tillage, sowing, varieties) on epidemiological risks
Disease management methods:
- Preventive strategies: varietal selection, residue management, crop establishment, adapted cultivation practices, etc.
- Contribution of decision-support tools (OAD)
- Rationalization of fungicide use: intervention thresholds, treatment windows, etc.
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Identify and distinguish between the main diseases of pea and faba bean, whether aerial or root-borne.
- Identify the risks of confusion between similar diseases and adopt a more vigilant approach
- Understand and analyze legume disease risk factors
- Select and implement management measures adapted to different disease situations
Hybrid format (1 day):
- Theoretical part: Technical inputs, case studies, interactive quizzes via Teams.
- Field practice: Analysis of plots, observation of development stages, diagnosis of crop accidents, exchanges with the trainer.
Active methods: Presentations, quizzes, debates, disease observation, exchanges of experience.
Evaluation: Quiz, disease recognition on a stand or in a plot (depending on the season), questions and answers, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.
Theoretical aids: Illustrated lectures, visual presentations, photographic documents, written material given to participants.
Diagnostic tools: Samples of diseased plants, recognition grids, decision-making tools for disease management.
Practical observation: Recognition of symptoms on samples or in real conditions (depending on the season).
Practical exchanges: Discussions, feedback between participants and trainer, case studies.
Agricultural technicians and advisors, Farmers and producers, Agricultural teachers and trainers, Agronomic and technical sales managers in agricultural distribution Quiz, disease recognition on a stand or in a plot (depending on the season), Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioning.If you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the Disability Advisor:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: c.caro@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 480€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/m7zxArcg4ffvqtjrk2zf47sw3nlcwvlkmrAt2z5yjvt2gmjp481x1qrv48gf2vcbpf3t3pj5hjng3mjxjm5wyvk3kjfgczdgnvcdc5d4lj5g4pj8 1 Jour Anne MOUSSART 23 Inter-company and intra-companyProject sheet
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Sed non risus. Suspendisse lectus tortor, dignissim sit amet, adipiscing nec, ultricies sed, dolor. Cras elementum ultrices diam. Maecenas ligula massa, varius a, semper congue, euismod non, mi. Proin porttitor, orci nec nonummy molestie, enim est eleifend mi, non fermentum diam nisl sit amet erat. Duis semper. Duis arcu massa, scelerisque vitae, consequat in, pretium a, enim. Pellentesque congue. Ut in risus volutpat libero pharetra tempor. Cras vestibulum bibendum augue. Praesent egestas leo in pede. Praesent blandit odio eu enim. Pellentesque sed dui ut augue blandit sodales. Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam nibh. Mauris ac mauris sed pede pellentesque fermentum. Maecenas adipiscing ante non diam sodales hendrerit.
Towards carbon neutrality with farms Maladies150,000 (CVO: €20,000)

Test title
text description
Title H2 List of links
Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text Descriptive text
KIT Petals - Rapeseed sclerotinia
Supply of a Petal KIT consisting of 10 Petri dishes containing a culture medium for detecting the presence of sclerotinia on rapeseed flowers. This kit can be used to determine the percentage of flowers contaminated at the start of flowering. This percentage is a good indicator of sclerotinia risk.
Price list
| Quantity | Price kit/unit (€) |
| Per unit | 27 € |
| From 5 to 9 kits | 26 € |
| From 10 to 19 kits | 25 € |
| 20 kits and more | 24 € |

Our other services
Building a localized supply chain
Terres Inovia can help you build a new, regionalized industry.From strategy to field…Oilseed impurities
Method used: in-house methodOilseed impurities ISO
Method used: NF EN ISO 658Water content ISO oilseeds
Method used: NF EN ISO 665Do you have a question?
Would you like to know more about this service or receive a quote? Send us your request!
Crop protection product mixtures
Find out if your crop protection product mix is authorized.
Terres Inovia has integrated its crops into the Internet application offered by ARVALIS-Institut du Végétal, which enables users to check the conformity of a mixture, or to construct a mixture from authorized products.

Diseases and plant pests of camelina
Generally speaking, camelina is not very susceptible to disease. However, some diseases can occasionally be observed, although to date their harmfulness remains relatively low and does not require any fungal intervention in vegetation.
Generally speaking, camelina is a crop with low susceptibility to disease. However, some diseases can occasionally be observed, although to date their harmfulness remains relatively low and does not require any fungal intervention in vegetation.
Whether grown as a main crop or as a summer catch crop, camelina shows the same behavior in the face of these diseases and parasites.
Cruciferous clubroot (Plasmodiophora brassicae)
Camelina can be affected by clubroot, a disease caused by the pathogen Plasmodiophora brassicae. This is a telluric disease with a host range extending to most species of the Brassicaceae family, including crops such as rape, turnip, cabbage and mustard.
Hernia can also infect certain weeds belonging to this family, such as ravenella, shepherd's purse or sanvia, all of which are potential reservoirs for its spread. Contamination occurs via mobile spores in the soil which, thanks to free water, penetrate the absorbent hairs of camelina roots and induce infection.
The main symptoms visible on the aerial parts are a temporary wilting of the foliage, particularly on hot days, and a slowdown in growth.
When affected plants are pulled up, the roots show characteristic deformations and swellings known as galls. These galls are responsible for the aerial symptoms, as they interfere with the absorption of water and nutrients from the soil. Initially firm and white on the inside, they gradually turn brown before cracking.

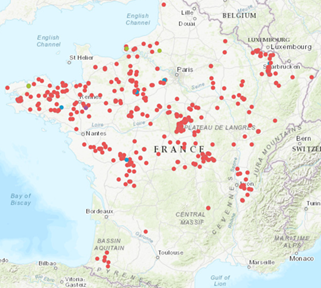
There are currently no effective chemical control methods. The development of the disease is favored by poor drainage of the plot, as well as by the absence of liming on acid soils. Once established, the disease persists in the soil, with spores remaining viable for up to 15 years. We therefore strongly advise against planting camelina on a plot known to be contaminated by this pathogen. Below is a map showing plots infected by clubroot, as reported online on the Terres Inovia website. https://www.terresinovia.fr/-/enquete-hernie-des-cruciferes

Downy mildew (Peronospora camelinae)
Mainly grown as a summer catch crop, camelina can be affected by mildew at the end of the cycle. This is the foliar disease most frequently observed on this crop, although its severity generally remains low and does not justify fungicide intervention.
Infection can be either localized or systemic. Symptoms observed on camelina include grayish-white mycelial growth on the underside of leaves, stems and siliques. Heavily affected plants may show distorted, twisted or bent growth.
The development of mildew is favored by temperatures between 15 and 23°C, combined with rainy spells generating high humidity, an essential condition for the spread of the disease.

White or albugo rust (Albugo candida)
White rust symptoms on camelina are similar to those observed on other crucifers. They take the form of white, powdery pustules, containing sporangia (reproductive structures), on the underside of leaves. At a more advanced stage, hypertrophied siliques or deformed inflorescences can also be observed.
Optimum development of the disease occurs between 10 and 18°C, with relative humidity above 90%.
It can be confused with mildew. However, it is possible to differentiate the two diseases by their symptoms: in the case of white rust, pustules are larger, well-defined and clearly visible, while mildew manifests itself through more diffuse spots and a more "powdery" appearance, linked to the presence of mycelium.
On camelina, mildew is observed more frequently than white rust.

Other secondary diseases
Other diseases have been observed on camelina, but their harmfulness is so low as to warrant no intervention in the crop. These include sclerotinia(Sclerotinia sclerotiorum), botrytis(Botrytis cinerea) and alternaria(Alternaria brassicae).
Rough broomrape (Phelipanche ramosa)
Orchardgrass is a non-chlorophyllous parasitic plant, present as seeds in the soil. They can only germinate in the presence of molecules emitted by the roots of certain plants, before attaching themselves to the latter.
It is capable of parasitizing many plant species, both winter and spring crops (rapeseed, hemp, tobacco, melon, sunflower, tomato...as well as camelina) and weeds (ammi majus, bedstraw, geraniums, erodium, cauliflower...).

Orchardgrass is highly invasive.
- It is capable of producing thousands of tiny seeds (0.2-0.3 mm) per plant, easily spread by wind, animals, farm machinery and so on.
- Seeds can live up to 10 years in the soil, and are resistant to passage through the digestive tract of animals.
- It has a very broad host spectrum (crops, weeds) and can synchronize its cycle with that of its host.
- It thrives in a wide range of pedoclimatic conditions.
Chemical or biocontrol methods are not currently authorized in France, and/or are ineffective in providing protection against stunted broomrape.
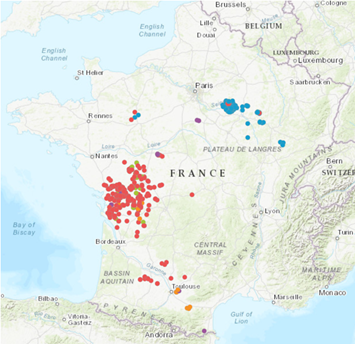
We therefore strongly advise against planting camelina on a plot known to be infested with stalked broomrape. Below, a map showing plots infected by stalked broomrape, identified following declarations made online on the Terres Inovia website. https://www.terresinovia.fr/web/guest/-/enquete-de-surveillance-orobanche-rameuse-participer-et-visualiser-les-zones-a-risque


Camelina editions
Our other articles
EvA - Aphanomyces risk assessment
The EvA tool enables you to quickly classify your plot as being at low or high risk, and thus guide you in your choices to preserve pea yield and plot health.
Aphanomyces is the most damaging telluric disease of peas. The EvA tool does not replace the Infectious Potential bioassay, but allows you to quickly classify your plot in a risk level and thus guide you in your choices to preserve pea yield and plot health.
Little information to fill in
The information you need to fill in is as follows: department, soil type, pea history and irrigation. These are few in number, but must be filled in very precisely.
A tool that can be used in most regions
The EvA tool was developed from a database containing information on 780 plots in the northern half of France, then validated on 120 plots, mainly in the Normandy and Centre-Val de Loire regions. This tool can be used in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté, Bretagne, Centre-Val de Loire, Grand Est, Hauts-de-France, Île-de-France, Normandie, Nouvelle-Aquitaine and Pays de la Loire regions.
Points of attention
At present, only the effect of a winter or spring pea crop on the evolution of a soil's Infectious Potential is known. The effect of other susceptible legumes has not yet been taken into account in this tool, for lack of data. Consequently, for plots that have received one or more susceptible legumes other than pea as a main, intermediate, associated or companion crop, the risk may be underestimated. Only the bioassay can be used to estimate the risk in these plots*.
*Susceptible legumes: lentil, alfalfa, chickling vetch, certain species/varieties of vetch (Access the test) "

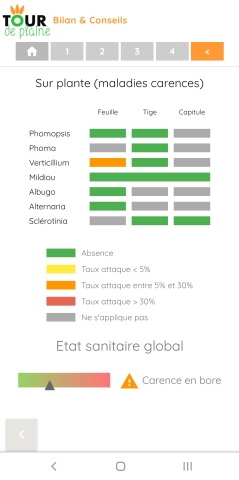
Tour de plaine tournesol
With Tour de Plaine, Terres Inovia accompanies you to each sunflower plot to establish a health diagnosis and give you the right advice for your next sunflower crop.
This connected application also works in the absence of a telephone network.
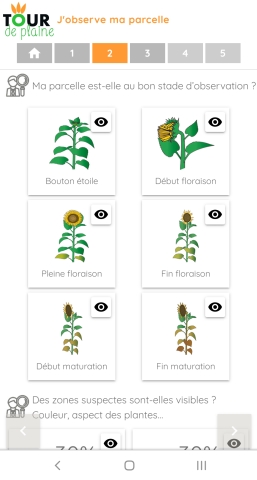
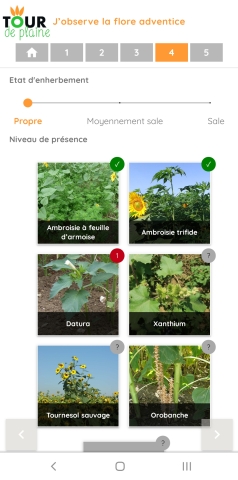
Your health check in 5 steps:
- I locate my plot
- I observe my plot
- I observe plants
- I observe weed flora
- Terres Inovia's assessment and advice

 Se connecter avec Facebook
Se connecter avec Facebook
 Se connecter avec Google
Se connecter avec Google




