Acacia
Composez le couvert d'interculture ou le couvert associé au colza adapté à votre situation
Un outil Excel d'aide à la décision, simple d'utilisation et entièrement paramétrable.
Consultez les fiches techniques des principales espèces de couverts
Conduite culturale : période de semis, implantation; caractéristiques : fourniture et piégeage d'azote, appétence limace etc; adaptation à la culture suivante
Composez votre mélange
Choix des espèces adaptées à vos objectifs et contraintes, composition du mélange selon des règles clé (nombre, complémentarité et compatibilité des espèces...) et ajustement des doses de semis
Retrouvez un grand nombre d'informations techniques sur votre mélange
Conseils pour l'implantation, simulation date de floraison et simulation économique


Cap Protéines Challenge: a 5th edition inspired by oilseeds!
The presentation of the shortlisted projects for the Cap Protéines Challenge 5 took place on December 12. The jury selected six teams to take part in the final on May 19, 2026 in Paris.
La présentation des projets des équipes présélectionnées pour le Cap Protéines Challenge 5 s’est tenue le 12 décembre dernier. Le jury en a retenu six, lesquelles participeront à la finale du 19 mai 2026 à Paris.
Pour cette nouvelle édition, 17 dossiers ont été déposés à l’issue du webinaire de lancement du 18 septembre 2025 avec des projets, lesquels répondent aux thématiques du concours. 8 d’entre eux ont passé la première étape de sélection pour ne laisser plus que 6 concurrents en lice, dont les idées ont séduit le jury d’experts le 12 décembre 2025. La finale se tiendra le 19 mai 2026 à Paris.
Des pommes noisettes à base de féverole

Fevie’s est une équipe d’ingénieurs de Sup’Biotech, qui développe des pommes noisettes à base de purée de féveroles. L’idée est d’introduire un nouvel accompagnement à base de légumineuses, sous une forme familière au sein des familles. Le but est d’en faciliter l’acceptabilité et l’introduction dans les habitudes de consommation.
Innovante, gourmande, rapide à préparer et riche en protéines (11,7g pour 100g de produit), la recette ne contient ni additifs ni conservateurs afin de proposer une recette simple et saine.
Bientôt une plateforme collaborative d’échanges de recettes durables

Cap Veggie est le premier organisme de formation professionnelle en cuisine végétarienne et à base de légumineuses pour la restauration collective et commerciale en grand volume. Aujourd’hui, Cap Veggie dispense des formations, participe à des missions de conseils et de la création de recettes.
Depuis quatre ans, Cap Veggie accompagne plus de mille chefs et équipes de cuisine, une vingtaine d’acteurs de l’agroalimentaire, et régale plus de 2 millions de convives avec ses recettes.
Au 2e semestre 2026, les porteurs du projet lanceront Mijote, la première plateforme web collaborative d’échanges de recettes durables pour les professionnels de la restauration collective.
Du sans gluten à base de protéagineux et oléagineux

Quatre entrepreneuses développent, produisent et commercialisent Floorish. Il s’agit de mixes de farine sans gluten à base de coproduits agroalimentaires revalorisés, issus de filières françaises. Les mixes sont à haute valeur nutritionnelle et enrichis grâce – entre autres – à l’utilisation de protéagineux et d’oléagineux. L’objectif est de réinventer le sans gluten en le rendant plus sain, plus gourmand et plus durable, sans compromis ni sur la texture ni sur le goût.
Les mixes pour pâtisseries et pains sont prêts à l’emploi et peuvent remplacer directement la farine de blé dans les recettes traditionnelles, sans ajustement de formulation.
Un jeu de plateau où l’on cultive des oléoprotéagineux

Cinq étudiants de l’école d’ingénieurs de Purpan propose Proté-Win, un jeu de plateau éducatif où chaque joueur incarne un agriculteur chargé de développer son exploitation en cultivant des oléoprotéagineux. Au fil des saisons, les joueurs doivent faire face aux aléas climatiques, aux maladies, aux fluctuations de marché et aux choix stratégiques de leurs voisins.
Entre négociations, alliances, bluffs et décisions économiques, chacun cherche à optimiser ses cultures, valoriser ses productions et progresser en compétences. Ludique et stratégique, le jeu permet de découvrir de manière simple et immersive les réalités de l’agriculture, la diversité des débouchés et le rôle essentiel des protéines végétales dans la filière.
Du pois chiche dans des plats préparés équilibrés

235 Eat vise à réinventer le prêt-à-cuisiner sec avec des préparations cœur de repas équilibrées, gourmandes et saines Les plus : un peu d’eau et hop, 5 minutes au micro-ondes !
Ce projet est porté par une jeune entrepreneuse passionnée d’innovation et avec l’ambition de lutter contre la malbouffe et le « sautage de repas » ; elle travaille dans des startups de l’agrifoodtech depuis huit ans.
La première gamme de ses prêt-à-cuisiner propose des préparations pour moelleux-repas salés ou sucrés, destinées aux jeunes actifs urbains et dont l’ingrédient clef est la farine de pois chiche. Le lancement est prévu en e-commerce à la fin du premier trimestre 2026.
Des "céréales" croquantes à base de pois chiche

BeanBuddiez est porté par un jeune doctorant à AgroParisTech. Il propose des "céréales" croquantes pour petit-déjeuner ou snack sain fabriquées à partir de pois chiches entiers, 100 % végétales, naturellement riches en protéines, en fibres, sans allergènes et avec une liste d’ingrédients courte. Deux déclinaisons de goûts sont imaginées : un Chico Pop enrobé de miel caramélisé et un Chico Pop à la cannelle.

Consult the latest issue of Arvalis & Terres Inovia infos
All four editions of the January 2026 issue of Arvalis & Terres Inovia infos are available online.
Les quatre éditions du numéro d'Arvalis & Terres Inovia infos de janvier 2026 sont disponibles et consultables en ligne.
Tournesol et oléoprotéagineux
- Tournesol : les variétés évaluées par Terres Inovia en 2025
- Implantation du tournesol : viser une levée avant le 1er mai
- Tournesol sauvage : faire front commun pour en venir à bout !
- Légumineuses de printemps : surveiller les thrips, sitones et pucerons dès la levée
- Pois et féveroles : les solutions disponibles pour protéger
Bonne lecture !
Les quatre éditions consultables en ligne

Fatty acids ISO s/seeds
Method used: NF EN ISO 17059 - NF EN ISO 12966-4

These services may be of interest to you
Building a localized supply chain
Terres Inovia can help you build a new, regionalized industry.From strategy to field…Oilseed impurities
Method used: in-house methodOilseed impurities ISO
Method used: NF EN ISO 658Water content ISO oilseeds
Method used: NF EN ISO 665Would you like a quote?
Would you like to know more about this service or receive a quote? Send us your request!
Successful pea and faba bean crops in the South-West
Our other training courses
Peas and faba beans: make the most of their potential in South-West systems
Crops with high agronomic and economic value, peas and field beans play a key role in rotations in the South-West. Adapted to the region's varied soils and climatic constraints, they can be used to diversify crop rotations while reducing inputs. To get the best out of them, careful management is essential: choice of plot, varieties, technical itinerary... This training course will guide you step-by-step in securing and optimizing these crops in your local context.
Program:
1. understanding how crops work in the South-West of France
- Pea and faba bean physiology: key stages, environmental requirements
- Agronomic, environmental and economic advantages in the regional context
2. crop management adapted to local conditions and associated decision rules
- Varietal selection adapted to the South-West climate
- Planting and sowing density according to regional soil types
- Phytosanitary protection: specific issues (Aphanomyces, Sclerotinia, aphids, etc.)
3 Diagnosis and management of hazards
- Identification of the main crop accidents observed in the region
4.value-adding and outlets
- Specific regional outlets (human food, export, local animal sectors)
- Storage and sorting strategies adapted to South-West markets
5.performance and sustainability
- Technical and economic analysis of itineraries in a local context
- Input reduction, nitrogen savings and benefits for the following crop
Training organized in collaboration with FILEG (free for their members)
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Identify the key success factors for pea and faba bean cultivation in the pedoclimatic context of the South-West,
- Choose and adapt technical itineraries according to soil, climate and local sanitary pressures,
- Diagnose the main crop failures in regional conditions,
- Assess the economic and environmental performance of these crops in a localized context.
Theoretical input: technical and scientific presentations adapted to the pedoclimatic context of the South-West.
Case studies: analysis of real situations encountered by farmers in the region.
Feedback from field experience: sharing of practices and solutions tried and tested by participants and trainer.
Interactive exchanges: time for questions, discussions and sharing between professionals.
Plot visit or field diagnosis (depending on the season): practical application of knowledge in the field.
Evaluation: quiz, questions and answers and individual satisfaction survey to measure skills acquisition.
The course is led by Quentin LAMBERT, a regional expert, guaranteeing local roots and a precise response to the specific challenges of the area.
Teaching aids: technical and summary documents given to participants (memo sheets, illustrated presentations, practical guides).
Visual illustrations: diagrams, photos and concrete examples to facilitate understanding of technical itineraries and diagnostics.
Case studies: analysis of real-life situations, diagnosis of crop accidents, and technico-economic performance studies.
Plot visits (where possible): direct observation of crops, soils and cultivation practices in real-life conditions.
Agricultural technicians and advisors, Farmers and producers, Agricultural teachers and trainers, Agronomic and technical sales managers in agricultural distribution, Agri-food / processing industry players Quizzes, Q&As and individual satisfaction surveys to measure skills acquisitionIf you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 480€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/38gvc6snjf8gw8lhmz6Acwbxnbrfcn5zmrvg4Ady4v3227brmvdhss5fnr3tmnry4vjd1pj5h35AAs5p4fm24wkplf7tm5t4l16A7mtfkbfw4pj8 1 Jour Quentin LAMBERT 95 Inter-company and intra-companyDare to use cover crops in your cropping systems
Direct seeding under plant cover (DMCS) combines the cessation of tillage with the establishment of permanent soil cover. Today, this is the most advanced form of conservation agriculture.
The agronomic benefits of these techniques are major, but only become real and lasting once farmers have mastered the system. Providing participants with the keys to the success of this system is the major challenge of this course.
Program:
Theoretical part (distance learning):
- Typology of plant cover crops (annual and permanent): species, associations, agronomic benefits
- Use and presentation of the ACACIA tool
- Construction of a coherent SDCV technical itinerary
- Rationalization of rotations
- Establishing, maintaining and regulating cover crops
- Nutrition, weed, pest and disease management
- Crop associations and agronomic performance
- Economic and environmental analysis of SDCV practices
Field part (either in Baziège (31) or in Nièvre (58)):
- Visit to SDCV plots
- Soil profile and interpretation
- Exchange of practices
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Explain the agronomic functioning of a direct seeding system under permanent cover
- Identify the plant species that can be used according to their objective and the local soil and climate context
- Develop a permanent soil cover strategy adapted to their cropping system;
- Master the key factors for a successful transition to direct seeding under permanent cover (rotation, fertility, cover crop management, pest management, etc.).
- Evaluate the economic and environmental impact of using direct seeding under cover.
Hybrid format:
- Distance learning theory (2 half-days): Technical inputs, case studies, interactive quizzes.
- Field practice (1 day): Analysis of plots, interpretation of soil profiles, exchanges with practicing farmers.
Active methods: Presentations, debates, questions and answers, practical work.
Evaluation: Quiz, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.
Theoretical support: Lectures, presentations, written material given to participants.
Management tool: Use and presentation for choosing and managing plant cover crops.
Plot visits: Observation and analysis of soil profiles in real-life situations.
Exchange of practices: Feedback and discussion between participants and trainers.
Farmers in a transition phase or wishing to optimize their practices; Agricultural technicians and advisors (cooperatives, chambers of agriculture, agri-supply companies); Agricultural high school teachers and agro-ecology trainers. Quiz, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioning
If you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the Disability Advisor:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 960€ TTC 5 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/mfb238dlgvr2c8btgjsAgsldgznhc8zAmz1xs8sp4r7f3mrrljgg37lyhb8f3ytk4nx2spj5hjrxms5blfwgc7sfl1xA35cymzx2g7lzgqzw4pj8 4 Jours Michael GELOEN 90 Inter-company and intra-companyEvaluation of legume susceptibility to aphanomyces, ascochytosis or botrytis
Disease susceptibility is assessed using a standardized bioassay under controlled conditions. Test varieties are inoculated with a suspension of pathogen spores, then incubated under conditions favorable to disease development. At the end of the test, the extent of symptoms is measured. Sensitivity and resistance controls are included in the test.

These services may be of interest to you
Building a localized supply chain
Terres Inovia can help you build a new, regionalized industry.From strategy to field…Oilseed impurities
Method used: in-house methodOilseed impurities ISO
Method used: NF EN ISO 658Water content ISO oilseeds
Method used: NF EN ISO 665Do you have a question?
Would you like to know more about this service or receive a quote? Send us your request!
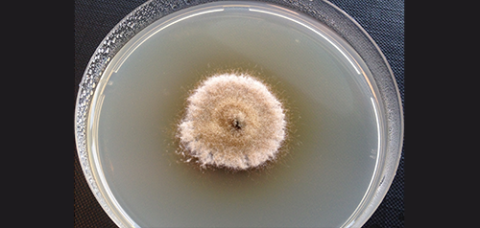
Fungal strain on culture medium
Supply of mycelial growth on culture medium for the fungal species described below.
Price: from 107€ excl. tax per strain
Alternaria brassicae, Alternaria brassicicola, Alternaria tenuissima, Aphanomyces euteiches, Aphanomyces cochlioides, Ascochyta pisi, Ascochyta fabae, Ascochyta rabiei, Botrytis cinerea, Botrytis fabae, Cladosporium sp, Cylindrosporium concentricum, Colletotrichum lini, Colletotrichum lupini, Epicoccum sp., Fusarium oxysporum, Fusarium solani, Leptosphaeria maculans, Leptosphaeria biglobosa, Leptosphaeria lindquistii, Macrophomina phaseolina, Penicillium sp., Phomopsis helianthi, Phoma medicaginis, Phomopsis phaseolorum, Rhizoctonia sp., Pythium sp., Pseudomonas syringae pv. pisi, Rhizopus sp., Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Sclerotinia trifoliorum, Septoria linicola, Septoria glycines, Stemphyllium sp., Trichoderma sp., Verticillium dahliae, Verticillium longisporum.
These services may be of interest to you
Building a localized supply chain
Terres Inovia can help you build a new, regionalized industry.From strategy to field…Oilseed impurities
Method used: in-house methodOilseed impurities ISO
Method used: NF EN ISO 658Water content ISO oilseeds
Method used: NF EN ISO 665Would you like a quote?
Would you like to know more about this service or receive a quote? Send us your request!
Aphanomyces in peas: testing the infectious potential of a soil
A biological test is carried out on a soil sample taken from the plot.
Price: from €129 excl. tax per soil
This test involves trapping the pathogen in susceptible pea plants growing in conditions favorable to the disease. The result is expressed on a scale from 0 (pathogen not detected in the sample) to 5 (heavily contaminated plot).

These services may be of interest to you
Building a localized supply chain
Terres Inovia can help you build a new, regionalized industry.From strategy to field…Oilseed impurities
Method used: in-house methodOilseed impurities ISO
Method used: NF EN ISO 658Water content ISO oilseeds
Method used: NF EN ISO 665Would you like a quote?
Would you like to know more about this service or receive a quote? Send us your request!
Pathological diagnosis on plant material
Diagnosis by macroscopic and microscopic observation, supplemented if necessary by molecular analysis and/or isolation of the pathogenic micro-organism on culture medium. The results are transmitted in the form of a report.
Price: from €268 excluding VAT

These services may be of interest to you
Building a localized supply chain
Terres Inovia can help you build a new, regionalized industry.From strategy to field…Oilseed impurities
Method used: in-house methodOilseed impurities ISO
Method used: NF EN ISO 658Water content ISO oilseeds
Method used: NF EN ISO 665Would you like a quote?
Would you like to know more about this service or receive a quote? Send us your request!


