The basics of rapeseed cultivation
Our other training courses
As rapeseed evolves, so does your knowledge!
With the rapid evolution of varieties, technical itineraries and decision-making tools, this training course offers a complete update on how to optimize rapeseed cultivation. Whether you're an experienced technician or a beginner, you'll discover the keys to success: genetic innovations, high-performance agronomic levers and benchmarks for making the right decisions at every stage of the campaign.
Day program :
- Yield development diagram and yield components
- Influence of different cultivation techniques
- Results of trials and surveys
- Main cropping decisions and decision rules
At the end of the course, participants will be able to:
- Identify rapeseed yield components and how they are determined
- Analyze the impact of cultivation practices on crop performance
- Select the varieties and inputs best suited to their soil and climate conditions and production objectives
- Adapt technical itineraries according to development stages and conditions encountered
- Make informed decisions throughout the growing season, based on technical, economic and agronomic data.
Active teaching methods: Technical presentations, case studies, feedback, alternating between theoretical input and feedback from field experience.
Evaluation: End-of-session quiz, questions and answers, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.
Theoretical support: Lectures, presentations, written material given to participants.
Exchange of practices: Feedback and debates between participants and trainers.
Interactivity: Quizzes, questions and answers, live exchanges with trainers.
Digital supports: Presentations and resources handed out after each session.
Technicians from development, economic organizations and the agri-supply industry. Teachers End-of-session quiz, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.If you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 480€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/gvhtcAdgnndxqAlgg8vAks6n3j6fg9tsj8vg4kzpmnxf4qk2gfhtmAsqkbyg5yzz4zcAspj5hjyAg9k5hbAg4sttlb3A4v544ncAwtcrljvAcpj8 1 Jour 40 Inter-company and intra-companySoybeans: Diagnosing climatic accidents
Our other training courses
Hail, heatstroke, thunderstorms... Do you really know how to recognize a climatic accident on soybeans?
Yield losses due to climatic hazards are on the rise, and an error in diagnosis can compromise compensation or effective intervention. This training course will give you the reflexes you need to accurately identify climatic damage and differentiate it from other causes (diseases, pests, deficiencies, etc.). Gain in responsiveness, reliability... and expertise.
Program:
1. soybean physiology
- Key stages in development
- Factors influencing yield production
2 Cultural management and critical points
- Emergence, flowering, pod filling
- Impact of practices on performance
3.crop accidents - typology and recognition
- Climatic hazards: hail, heat stroke, excess water, strong winds
- Pest and disease damage
- Nutritional deficiencies and abiotic stress
- Phytotoxicities (herbicides)
- Other observable anomalies
On completion of the course, participants will be able to:
- Explain the key elements of soybean physiology in relation to crop management and yield formation.
- Identify sensitive phases in soybean development, from emergence to harvest.
- Diagnose the main climatic accidents (hail, wind, heat, storms, etc.).
- Differentiate between other causes of damage: diseases, pests, nutritional deficiencies, phytotoxicities, etc.
Face-to-face format:
-
Classroom contributions: Presentation of the types of climatic accidents, case studies, application exercises.
-
Field observation (if conditions are favorable): Analysis of real-life situations in the field (depending on date and availability of sites).
Active methods: Presentations, discussions, questions and answers, case studies, applied diagnostics.
Evaluation: Quiz, questions and answers, practical exercises, self-assessment, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.
Theoretical support: Presentations, lectures, summary documents given to participants.
Case studies: Real-life situations analyzed collectively, according to context.
Exchange of practices: Feedback between participants and trainers to enrich diagnoses.
Agricultural technicians and advisors, Employees of agricultural cooperatives and sales outlets (agronomy and technical sales departments), Agricultural insurance experts or inspectors, Soybean industry managers, Teachers and trainers, Farmers looking to improve their skills or carry out self-diagnosis on their plots of land Quiz, Q&A, self-positioning, individual satisfaction survey.If you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 240€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/mvwgk65Akbww49dtgfA2mAdtjyytqs5rj7zt14cp38wx2n5knz2g3s5vk25fg7lzjjlAcpj5hjcxc55rfncs9Ack38kAgvd2jqvxqrsA4Axvcpj8 1 Jour 34 Inter-company and intra-companySunflower: Diagnosing climatic accidents
Our other training courses
Climatic events regularly have an impact on sunflower yields. For insurers and field technicians alike, it is essential to distinguish precisely between weather-related damage and that caused by other factors (diseases, pests, deficiencies, phytotoxicities). This training course will give you the keys to accurately observe, analyze and diagnose sunflower claims, in order to inform your decisions and avoid misinterpretations.
The program includes
- Elements of physiology: key stages of the crop
- Sensitive points in crop management
- Main crop accidents: Weather-related accidents, Pest damage, Disease damage, Nutritional deficiencies, Herbicide-related phytotoxicities, Other accidents
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Understand the key elements of sunflower physiology influencing crop management and yield formation.
- Identify sensitive points in sunflower cultivation, from emergence to harvest, in relation to growing conditions.
- Diagnose the main climatic accidents that can affect sunflowers: hail, wind, heat stroke, storms, etc.
- Recognize other accidents that can affect sunflower crops: pests, diseases, deficiencies, etc.
Face-to-face format:
-
Theory in the classroom: Technical inputs, case studies, interactive exchanges.
-
Practical in the field (subject to favorable conditions): Diagnosis of plots, observation of climatic accidents (subject to favorable conditions), collective analysis of situations encountered.
Active methods: Presentations, discussions, questions and answers, role-playing, analysis of real-life cases.
Evaluation: Quiz, questions and answers, self-assessment at start and end of training, individual satisfaction survey.
Theoretical support: Lectures, presentations, written material given to participants.
Observation tools: Diagnostic grids and damage recognition sheets.
Plot visits: Analysis of accidents under real conditions (climate, phytotoxicity, diseases, etc.) if present.
Practical exchanges: Feedback and discussions between participants and trainer to enhance diagnosis.
Agricultural technicians and advisors, Employees of agricultural cooperatives and sales outlets (agronomy and technical sales departments), Agricultural insurance experts or inspectors, Soybean industry managers, Teachers and trainers, Farmers seeking to improve their skills or carry out self-diagnosis on their plots of land. Quiz, Q&A, self-assessment at start and end of training, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioning.If you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 480€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/3vcgAmsdjq72385l3rk2qz5w4jbg3rk2jvyt1ys2lbkA7ykfpbAd2ytnj8xw3k62j2ytqpj5hj7dq6d3kfzwwy52hfjh46jljvzdgz52jyvw4pj8 1 Jour Matthieu ABELLA 33 Inter-company and intra-companySUN'Live: The essentials of sunflower management in 7 sequences
Our other training courses
Would you like to learn more about sunflower cultivation? SUN live is a distance learning course featuring 7 sequences led by Terres Inovia experts, covering the key practices and moments essential to sunflower success. It is designed to enable you to master the fundamental aspects of the crop, whether this is your first discovery or a refresher course.
The program includes
Sequence 1: Planting and pests
- Management of intercropping (including cover crops) prior to sunflower cultivation.
- Techniques for successfully establishing a robust sunflower crop in the face of summer constraints.
- Encourage uniform planting and deep rooting.
- Identification of early-cycle pests, assessment of their harmfulness, and presentation of possible control methods.
Sequence 2: Positioning in crop rotation and economic assessment
- Agro-economic characteristics of the sunflower species: a robustness conditioned by careful and optimized cultivation.
- Optimizing sunflower's place in rotations
- What economic impact does sunflower have on cropping systems?
Sequence 3: Weed control
- Complementarity between agronomic, chemical and mechanical solutions
- Presentation of herbicide solutions and programs
- Targets, spectrum, efficacy, selectivity and conditions of use of the main herbicides for sunflower.
Sequence 4: Fertilization
- Specificities of sunflower with regard to nitrogen supply and calculating the dose to be applied
- Rationale for phospho-potassium fertilization
- Sunflower needs in trace elements; focus on boron and molybdenum
Sequence 5: Harvesting and production quality
- Choosing the right time to harvest.
- Presentation of suitable harvesting equipment.
- Good conservation and storage practices.
Sequence 6: Ecophysiology and water efficiency
- Distribution of water requirements throughout the cycle.
- Importance of early-flowering leaf area index and leaf area duration.
- Irrigating sunflowers: an opportunity to be seized.
- Identification of key periods in the cycle and climatic requirements for each growth stage.
- Factors influencing yield and oil content.
Sequence 7: Diseases and cumana broomrape
- Recognition of the main diseases, biological cycle, harmfulness, protection methods, warning and decision-making tools.
- Orobanche cumana: recognition, harmfulness, monitoring and management of affected areas in France
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Identify the key stages of the crop, from planting to harvest, and evaluate their success.
- Diagnose the main problems affecting sunflower cultivation.
- Understand and use decision-making tools to help the crop reach its full potential and maximize profitability.
100% digital format: Remote training, accessible from any connected computer.
Active pedagogy: Technical presentations, case studies, feedback, analysis of real-life situations.
Evaluation: Quiz at each session, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.
Online sessions: 7 sequences of 2 hours on Teams, led by Terres Inovia expert engineers.
Theoretical support: Technical presentations, summary documents, decision-making tools (e.g. fertilization calculations, pest and disease identification grids).
Interactivity: Quizzes, live questions and answers, exchanges with trainers and participants.
Digital support: Presentations and resources handed over after each session.
Technicians from development, economic and agri-supply organizations. Farmers. Teachers Quiz at each session, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioningIf you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 960€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/4vjvAl6wk8mhs76Am85vm6kqgvct15dt3rAhgnl3kj7A7wk2krvfgrrAjbdvqwclg8kAspj5hjhxkztppbsdc7lzjnmwc56pjbhfkz6qmz3Acpj8 7 Jours 29 Inter-company and intra-companyCOLZA'Live: Understanding rapeseed crop management in 7 sequences
Our other training courses
Whether you're a beginner or want to update your knowledge, COLZA Live training offers you a complete understanding of rapeseed growing. Thanks to 7 short, interactive sequences, led by experts, you can acquire the essential skills to optimize your farming practices, all in digital format.
Program:
Sequence 1: Introduction to the crop and planting (April 7, 2026, 9 to 11 a.m.)
- Global context of rapeseed cultivation and associated agricultural issues
- Identification of stages in the rapeseed crop cycle and phenological stages.
- The challenges of rapeseed establishment, the benefits of a robust rapeseed and the key conditions to be achieved, the keys to choosing the optimum establishment techniques depending on the context.
Sequence 2: Fertilization (April 8, 2026, 9 a.m. to 11 a.m.)
- Rapeseed specificities with regard to nitrogen supply
- Calculation of spring nitrogen dose (Réglette azote colza®) and choice of fractioning strategy
- Rationalization of phosphate, potassium and sulfur fertilization
- Rapeseed needs in trace elements; focus on boron and molybdenum
Sequence 3: Weed control (April 10, 2026, 9 a.m. to 11 a.m.)
- Description of the main agronomic control levers
- Development of herbicide control strategies adapted to weed flora.
- Grass control: Ray-Grass & Vulpin
- Presentation of mechanical control methods and mixed weed control strategies.
Sequence 4: Spring diseases (April 14, 2026, 9am to 11am)
- Reminder of the main spring diseases Sclerotinia, Oidium, Alternaria, Mycosphaerella, Phoma ...
- Study of the biological cycle and harmfulness of these diseases.
- Control methods available as part of integrated crop protection.
Sequence 5: Spring pests (April 29, 2026, 9 to 11 a.m.)
- Presentation of the different spring pests: description and development cycle.
- Presentation of the main management strategies
- Presentation of preventive measures (agronomic levers) to limit the impact of pests.
- Nuisibility, risk assessment during the season (presentation of Decision Support Tools and decision rules) and decision-making.
- Choice of insecticides
- Prospects for biocontrol solutions
- Presentation of the main natural enemies.
Sequence 6: Harvesting and yield components and ecophysiological aspects (May 19, 2026, 9 to 11 a.m.)
- Strategies to limit harvest losses.
- Presentation of the swathing technique to optimize rapeseed harvesting.
- Explanation of the year's yields: rapeseed yield components and favorable factors.
Sequence 7: Autumn pests (June 23, 2026, 9 a.m. to 11 a.m.)
- Presentation of the different autumn pests: description and development cycle.
- Presentation of the main management strategies.
- Preventive measures: levers to mobilize upstream to limit risk during the season.
- Nuisibility and risk assessment during the season (presentation of decision-support tools and decision rules).
- Choice of insecticides and slug pellets.
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Understand and master rapeseed cultivation techniques
- Make informed decisions to optimize the crop
- Evaluate the success of rapeseed cultivation
- Optimize rapeseed planting
- Apply effective weed control strategies
- Managing fall and spring pests
- Optimize rapeseed fertilization
- Controlling spring diseases
- Minimize harvest losses
100% digital format: Remote training, accessible from any connected computer.
Active pedagogy: Technical presentations, case studies, feedback.
Evaluation: End-of-session quiz, questions and answers, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.
Online sessions: 7 sequences of 2 hours on Teams, led by Terres Inovia expert engineers.
Theoretical support: Presentations, technical documents, ADO proposals.
Interactivity: Quizzes, questions and answers, live exchanges with trainers.
Digital support: Presentations and resources handed over after each session.
Technicians from development, economic and agri-supply organizations. Farmers. Teachers Quiz during each session, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioning.If you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 960€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/g8yt16bAkfctmrlrkbmdmsd4gvAw45c4gzzg7vzz3ncw49smljrxmszz47vA956hmzrvcpj5hj62c85cmjsf48jpgnAA3wkjf8md2rdzhb32cpj8 7 Jours 28 Inter-company and intra-companyHarvesting camelina
Although camelina has a low risk of shattering at maturity, it is particularly sensitive to post-ripening losses: its seeds are highly susceptible to shattering during cutting, to breakage during threshing, and to direct losses in the field.
General
Although camelina has a low risk of shattering at maturity, it is particularly sensitive to post-ripening losses: its seeds are highly susceptible to shattering during cutting, to breakage during threshing, and to direct losses in the field.
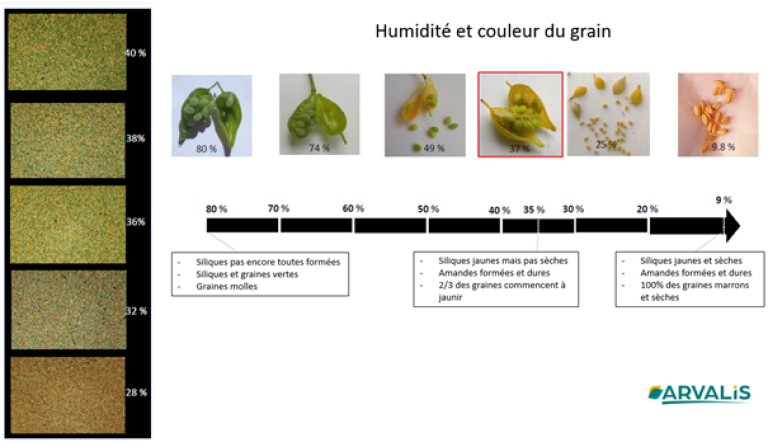
Camelina reaches maturity when the siliques change color from lemon-yellow to brownish. At this stage, seed moisture is generally between 8 and 10%. They detach easily from their shells under light manual pressure.
At this stage, it is crucial to intervene quickly, and harvesting should ideally be carried out within 7 to 10 days to limit dehiscence losses.
To guarantee good seed conservation and optimal storage conditions, humidity at harvest must not exceed 9%.
In the presence of fresh impurities (green matter), we recommend pre-sorting within 24 hours of harvesting, to limit temperature rise and reduce overall batch humidity.
If, after sorting, humidity remains above 9%, drying is necessary to avoid risks of deterioration (heating, fungal development, etc.).
Please note: under a contract with SAIPOL, the impurity content must not exceed 2%.
The graph below illustrates the evolution of seed moisture as a function of color.
Setting up the combine harvester
As camelina is a small-seed crop, it is essential to adapt combine settings and forward speed (ideally between 3 and 4 km/h) to limit losses.
Main recommended settings:
- Cutterbar: adjust the height just below the lowest siliques to minimize losses at the base.
- Reel: moderate speed, between 600 and 700 rpm, to limit silique breakage.
- Thresher / concave: initial spacing of 15 to 20 mm. Start with a setting similar to that used for cereals. If unthreshed whole siliques are found in the hopper, slightly increase the beater speed or reduce the spacing between beater and concave.
- Sieves :
- Lower sieve: as closed as possible.
- Upper sieve: initial opening 20%, to be adjusted according to sorting quality and throughput.
- Sieves :
- Ventilation: very low air flow to avoid losses, as camelina seeds are very light.
A combine adjustment guide published by SAIPOL with recommendations from Nicolas Thibaud is available on request.

A video is also available:
Mowing - swathing
Swathing mainly concerns camelina crops grown as summer catch crops. At maturity, the crop is generally upright, which makes swathing much easier. Before mowing, it is imperative to ensure that the weather conditions over the next few days will be dry, in order to guarantee proper drying of the swath and avoid any delay in harvest recovery.
In fact, swathing should ideally take place 4 to 6 days after mowing, to avoid increasing losses and degrading seed quality.
This practice has three main objectives:
- Bring forward the harvest date, with an estimated gain of around 10 days in October;
- To improve harvest quality, by enabling faster drying of the seeds in the swath;
- Reduce weed infestation at the end of the cycle.
The plot is ready to be swathed when around 75% of siliques have turned yellow, corresponding to a seed moisture level of around 30%, generally reached 2 to 3 weeks after the last flower.

The cutting height should be just below the lowest siliques (i.e. between 15 and 20 cm) to ensure good aeration of the swath.
It is strongly recommended not to turn the swath, in order to limit ginning losses.
The swath is then harvested using a combine harvester, around 4 to 6 days after mowing, once drying conditions are optimal.

Camelina editions
Our other articles
Weeding camelina
Camelina nutrition
[COMING SOON] When to sow to harvest sunflowers
Estimate the sunflower harvesting period, according to your location, based on your choice of variety and your planned sowing date.
This tool will tell you how much risk you are taking at harvest, depending on your sowing date and criteria.
This tool is designed for sunflower as a main crop, not as a catch crop. It is based on frequent climatic data and does not incorporate weather data for the current season.