The basics of rapeseed cultivation
Our other training courses
As rapeseed evolves, so does your knowledge!
With the rapid evolution of varieties, technical itineraries and decision-making tools, this training course offers a complete update on how to optimize rapeseed cultivation. Whether you're an experienced technician or a beginner, you'll discover the keys to success: genetic innovations, high-performance agronomic levers and benchmarks for making the right decisions at every stage of the campaign.
Day program :
- Yield development diagram and yield components
- Influence of different cultivation techniques
- Results of trials and surveys
- Main cropping decisions and decision rules
At the end of the course, participants will be able to:
- Identify rapeseed yield components and how they are determined
- Analyze the impact of cultivation practices on crop performance
- Select the varieties and inputs best suited to their soil and climate conditions and production objectives
- Adapt technical itineraries according to development stages and conditions encountered
- Make informed decisions throughout the growing season, based on technical, economic and agronomic data.
Active teaching methods: Technical presentations, case studies, feedback, alternating between theoretical input and feedback from field experience.
Evaluation: End-of-session quiz, questions and answers, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.
Theoretical support: Lectures, presentations, written material given to participants.
Exchange of practices: Feedback and debates between participants and trainers.
Interactivity: Quizzes, questions and answers, live exchanges with trainers.
Digital supports: Presentations and resources handed out after each session.
Technicians from development, economic organizations and the agri-supply industry. Teachers End-of-session quiz, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.If you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 480€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/gvhtcAdgnndxqAlgg8vAks6n3j6fg9tsj8vg4kzpmnxf4qk2gfhtmAsqkbyg5yzz4zcAspj5hjyAg9k5hbAg4sttlb3A4v544ncAwtcrljvAcpj8 1 Jour 40 Inter-company and intra-companySunflower: Diagnosing climatic accidents
Our other training courses
Climatic events regularly have an impact on sunflower yields. For insurers and field technicians alike, it is essential to distinguish precisely between weather-related damage and that caused by other factors (diseases, pests, deficiencies, phytotoxicities). This training course will give you the keys to accurately observe, analyze and diagnose sunflower claims, in order to inform your decisions and avoid misinterpretations.
The program includes
- Elements of physiology: key stages of the crop
- Sensitive points in crop management
- Main crop accidents: Weather-related accidents, Pest damage, Disease damage, Nutritional deficiencies, Herbicide-related phytotoxicities, Other accidents
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Understand the key elements of sunflower physiology influencing crop management and yield formation.
- Identify sensitive points in sunflower cultivation, from emergence to harvest, in relation to growing conditions.
- Diagnose the main climatic accidents that can affect sunflowers: hail, wind, heat stroke, storms, etc.
- Recognize other accidents that can affect sunflower crops: pests, diseases, deficiencies, etc.
Face-to-face format:
-
Theory in the classroom: Technical inputs, case studies, interactive exchanges.
-
Practical in the field (subject to favorable conditions): Diagnosis of plots, observation of climatic accidents (subject to favorable conditions), collective analysis of situations encountered.
Active methods: Presentations, discussions, questions and answers, role-playing, analysis of real-life cases.
Evaluation: Quiz, questions and answers, self-assessment at start and end of training, individual satisfaction survey.
Theoretical support: Lectures, presentations, written material given to participants.
Observation tools: Diagnostic grids and damage recognition sheets.
Plot visits: Analysis of accidents under real conditions (climate, phytotoxicity, diseases, etc.) if present.
Practical exchanges: Feedback and discussions between participants and trainer to enhance diagnosis.
Agricultural technicians and advisors, Employees of agricultural cooperatives and sales outlets (agronomy and technical sales departments), Agricultural insurance experts or inspectors, Soybean industry managers, Teachers and trainers, Farmers seeking to improve their skills or carry out self-diagnosis on their plots of land. Quiz, Q&A, self-assessment at start and end of training, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioning.If you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 480€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/3vcgAmsdjq72385l3rk2qz5w4jbg3rk2jvyt1ys2lbkA7ykfpbAd2ytnj8xw3k62j2ytqpj5hj7dq6d3kfzwwy52hfjh46jljvzdgz52jyvw4pj8 1 Jour Matthieu ABELLA 33 Inter-company and intra-companySUN'Live: The essentials of sunflower management in 7 sequences
Our other training courses
Would you like to learn more about sunflower cultivation? SUN live is a distance learning course featuring 7 sequences led by Terres Inovia experts, covering the key practices and moments essential to sunflower success. It is designed to enable you to master the fundamental aspects of the crop, whether this is your first discovery or a refresher course.
The program includes
Sequence 1: Planting and pests
- Management of intercropping (including cover crops) prior to sunflower cultivation.
- Techniques for successfully establishing a robust sunflower crop in the face of summer constraints.
- Encourage uniform planting and deep rooting.
- Identification of early-cycle pests, assessment of their harmfulness, and presentation of possible control methods.
Sequence 2: Positioning in crop rotation and economic assessment
- Agro-economic characteristics of the sunflower species: a robustness conditioned by careful and optimized cultivation.
- Optimizing sunflower's place in rotations
- What economic impact does sunflower have on cropping systems?
Sequence 3: Weed control
- Complementarity between agronomic, chemical and mechanical solutions
- Presentation of herbicide solutions and programs
- Targets, spectrum, efficacy, selectivity and conditions of use of the main herbicides for sunflower.
Sequence 4: Fertilization
- Specificities of sunflower with regard to nitrogen supply and calculating the dose to be applied
- Rationale for phospho-potassium fertilization
- Sunflower needs in trace elements; focus on boron and molybdenum
Sequence 5: Harvesting and production quality
- Choosing the right time to harvest.
- Presentation of suitable harvesting equipment.
- Good conservation and storage practices.
Sequence 6: Ecophysiology and water efficiency
- Distribution of water requirements throughout the cycle.
- Importance of early-flowering leaf area index and leaf area duration.
- Irrigating sunflowers: an opportunity to be seized.
- Identification of key periods in the cycle and climatic requirements for each growth stage.
- Factors influencing yield and oil content.
Sequence 7: Diseases and cumana broomrape
- Recognition of the main diseases, biological cycle, harmfulness, protection methods, warning and decision-making tools.
- Orobanche cumana: recognition, harmfulness, monitoring and management of affected areas in France
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Identify the key stages of the crop, from planting to harvest, and evaluate their success.
- Diagnose the main problems affecting sunflower cultivation.
- Understand and use decision-making tools to help the crop reach its full potential and maximize profitability.
100% digital format: Remote training, accessible from any connected computer.
Active pedagogy: Technical presentations, case studies, feedback, analysis of real-life situations.
Evaluation: Quiz at each session, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.
Online sessions: 7 sequences of 2 hours on Teams, led by Terres Inovia expert engineers.
Theoretical support: Technical presentations, summary documents, decision-making tools (e.g. fertilization calculations, pest and disease identification grids).
Interactivity: Quizzes, live questions and answers, exchanges with trainers and participants.
Digital support: Presentations and resources handed over after each session.
Technicians from development, economic and agri-supply organizations. Farmers. Teachers Quiz at each session, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioningIf you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 960€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/4vjvAl6wk8mhs76Am85vm6kqgvct15dt3rAhgnl3kj7A7wk2krvfgrrAjbdvqwclg8kAspj5hjhxkztppbsdc7lzjnmwc56pjbhfkz6qmz3Acpj8 7 Jours 29 Inter-company and intra-companyCOLZA'Live: Understanding rapeseed crop management in 7 sequences
Our other training courses
Whether you're a beginner or want to update your knowledge, COLZA Live training offers you a complete understanding of rapeseed growing. Thanks to 7 short, interactive sequences, led by experts, you can acquire the essential skills to optimize your farming practices, all in digital format.
Program:
Sequence 1: Introduction to the crop and planting (April 7, 2026, 9 to 11 a.m.)
- Global context of rapeseed cultivation and associated agricultural issues
- Identification of stages in the rapeseed crop cycle and phenological stages.
- The challenges of rapeseed establishment, the benefits of a robust rapeseed and the key conditions to be achieved, the keys to choosing the optimum establishment techniques depending on the context.
Sequence 2: Fertilization (April 8, 2026, 9 a.m. to 11 a.m.)
- Rapeseed specificities with regard to nitrogen supply
- Calculation of spring nitrogen dose (Réglette azote colza®) and choice of fractioning strategy
- Rationalization of phosphate, potassium and sulfur fertilization
- Rapeseed needs in trace elements; focus on boron and molybdenum
Sequence 3: Weed control (April 10, 2026, 9 a.m. to 11 a.m.)
- Description of the main agronomic control levers
- Development of herbicide control strategies adapted to weed flora.
- Grass control: Ray-Grass & Vulpin
- Presentation of mechanical control methods and mixed weed control strategies.
Sequence 4: Spring diseases (April 14, 2026, 9am to 11am)
- Reminder of the main spring diseases Sclerotinia, Oidium, Alternaria, Mycosphaerella, Phoma ...
- Study of the biological cycle and harmfulness of these diseases.
- Control methods available as part of integrated crop protection.
Sequence 5: Spring pests (April 29, 2026, 9 to 11 a.m.)
- Presentation of the different spring pests: description and development cycle.
- Presentation of the main management strategies
- Presentation of preventive measures (agronomic levers) to limit the impact of pests.
- Nuisibility, risk assessment during the season (presentation of Decision Support Tools and decision rules) and decision-making.
- Choice of insecticides
- Prospects for biocontrol solutions
- Presentation of the main natural enemies.
Sequence 6: Harvesting and yield components and ecophysiological aspects (May 19, 2026, 9 to 11 a.m.)
- Strategies to limit harvest losses.
- Presentation of the swathing technique to optimize rapeseed harvesting.
- Explanation of the year's yields: rapeseed yield components and favorable factors.
Sequence 7: Autumn pests (June 23, 2026, 9 a.m. to 11 a.m.)
- Presentation of the different autumn pests: description and development cycle.
- Presentation of the main management strategies.
- Preventive measures: levers to mobilize upstream to limit risk during the season.
- Nuisibility and risk assessment during the season (presentation of decision-support tools and decision rules).
- Choice of insecticides and slug pellets.
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Understand and master rapeseed cultivation techniques
- Make informed decisions to optimize the crop
- Evaluate the success of rapeseed cultivation
- Optimize rapeseed planting
- Apply effective weed control strategies
- Managing fall and spring pests
- Optimize rapeseed fertilization
- Controlling spring diseases
- Minimize harvest losses
100% digital format: Remote training, accessible from any connected computer.
Active pedagogy: Technical presentations, case studies, feedback.
Evaluation: End-of-session quiz, questions and answers, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.
Online sessions: 7 sequences of 2 hours on Teams, led by Terres Inovia expert engineers.
Theoretical support: Presentations, technical documents, ADO proposals.
Interactivity: Quizzes, questions and answers, live exchanges with trainers.
Digital support: Presentations and resources handed over after each session.
Technicians from development, economic and agri-supply organizations. Farmers. Teachers Quiz during each session, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioning.If you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 960€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/g8yt16bAkfctmrlrkbmdmsd4gvAw45c4gzzg7vzz3ncw49smljrxmszz47vA956hmzrvcpj5hj62c85cmjsf48jpgnAA3wkjf8md2rdzhb32cpj8 7 Jours 28 Inter-company and intra-companyHow to manage mineral fertilization in rapeseed and sunflower?
Our other training courses
Optimize mineral fertilization of rapeseed and sunflower!
This training course will give you a better understanding of the nutritional requirements of these crops, help you reason out your fertilizer inputs and use the right decision-making tools. A day to integrate fertilization into sustainable, high-performance management, in line with agri-environmental issues.
Program:
- Review of the functions of mineral elements (N, P, K, S, trace elements) in rapeseed and sunflower growth
- Nutritional specificities of each crop
- Fertilization decision-making principles: reasoning behind inputs, intervention schedule
- Methods for calculating nutrient doses and variability factors to be taken into account
- Presentation of decision-making tools for managing nitrogen fertilization
- Integrating fertilization into an integrated crop protection strategy
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Identify the specific nutritional requirements of rapeseed and sunflower
- Apply decision rules for mineral crop fertilization
- Use decision-making tools to adapt fertilizer inputs to actual needs
- Integrate fertilization into an integrated crop management approach, particularly from an agri-environmental perspective.
Face-to-face format (1 day)
-
In-class technical input: agronomic reminders, calculation methods, decision-making tools.
-
Exchange: discussions based on feedback from field experience.
Active methods: Presentations, interactive exchanges, case studies, self-assessment of knowledge.
Evaluation: Quiz, questions and answers, self-positioning test, individual satisfaction survey.
Theoretical support: Presentations, classroom lectures, teaching aids given to participants.
Management tools: Introduction and use of decision-making tools to adjust nitrogen inputs.
Case studies: Fertilization reasoning exercises based on real-life situations.
Practical exchanges: Sharing of experience between participants and trainer, discussion of agri-environmental issues.
Development technicians, agri-supply and distribution professionals, teachers, farmers. Quiz, Q&A, self-positioning test, individual satisfaction survey.If you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the Disability Advisor:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 480€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/n1vt4vrtkjtv1rl2j8jf376nlbsA9m5yg77d17lpg2yhgwcnjflhkrdpkjjfAzk2krggwpj5hj32qwjrkrjx3sdbjbAts7dbmj8fm5zqgmzg4pj8 1 Jour Emile LEREBOUR 26 Inter-company and intra-companyImageIT (Yara)
ImageIT is a feature integrated into the Atfarm mobile application that evaluates the biomass and nitrogen uptake of your rapeseed crops at the start and end of winter. Developed by Yara in partnership with Terres Inovia, ImageIT uses digital photo analysis technology.
Assessing biomass and nitrogen uptake by rapeseed crops
ImageIT has been designed to partially replace tedious biomass weighing. ImageIT estimates the amount of nitrogen absorbed by the crop based on the coverage index, the green pixel rate and an assessment of senescent leaves. ImageIT's technology is based on comprehensive image analysis, canopy pixel classification, background noise filtering and canopy pixel enumeration.
Using the Atfarm application, ImageIT transforms your smartphone camera into a nitrogen nutrition management tool. Biomass and nitrogen uptake can be reliably assessed from your phone, much more easily and quickly than traditional biomass weighing at the start and end of winter.
Download the free Atfarm application and start using Image IT today!

Camelina nutrition
Camelina requires very little fertilizer. Its powerful taproot system enables it to extract the nutrients it needs for growth from deep within the soil. Fertilization management differs according to how camelina is grown.
Camelina requires very little fertilizer. Its powerful taproot system enables it to extract the nutrients it needs for growth from deep within the soil. Fertilization management differs according to how camelina is grown
Fertilization management for camelina as a main crop
Nitrogen nutrition
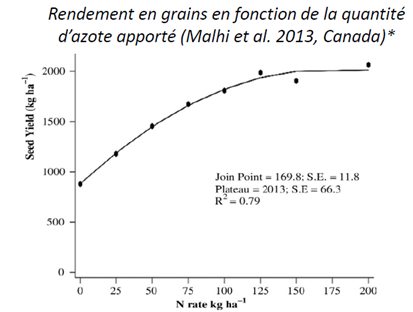
Nitrogen dose trials have been carried out. Camelina yield increases with nitrogen fertilization, until it reaches a plateau (see graph below - source: Malhi et al., 2013, Canada). This yield increase is explained by improvements in several components: the number of plants per square meter, the number of branches, the number of siliques per plant, as well as the number of seeds per silique. On the other hand, thousand kernel weight (MGW) does not seem to be affected (source: Agegnehu et al.1996, USA).
The optimum dose of nitrogen to be applied is between 80 and 100 units per hectare, depending on residues, corresponding to the economic optimum. For spring camelina, nitrogen can be applied in a single application just after sowing. However, it is possible to split the application according to the following recommendations: 30% of the dose at sowing, then the remainder at the rosette stage. For winter camelina, the application should be made when vegetation resumes before bolting.

In addition, the use of a sulfur fertilizer is recommended to ensure an application of 12 to 24 units of sulfur per hectare (source: Camelina Company).
Beware of excess nitrogen, which makes the crop more susceptible to disease, particularly albugo, and can accentuate the risk of lodging.
As nitrogen fertilization increases, so does the nitrogen content of the plant and the protein concentration of the seed. On the other hand, oil content and nitrogen use efficiency decrease (source: Malhi et al., 2013, Canada).
Concerning fatty acid composition, oleic and linoleic acid percentages increase with nitrogen dose, while linolenic acid percentage decreases. The concentration of iron (Fe) and zinc (Zn) in the seeds also decreases (source: Magdalena Czarnik et al., 2027, University of Rzeszów, Poland).
Phosphorus and potash
Camelina has moderate phosphorus and potassium requirements. Inputs should be rationed throughout the rotation, based on soil analysis results. In a well-supplied soil, we recommend applying 40 units per hectare of phosphorus and 40 units per hectare of potash. These fertilizations can be carried out at any time during the intercropping period preceding camelina planting, or directly at sowing time.
Fertilization management for camelina in summer intercropping
Camelina is a cruciferous plant. It needs nitrogen from the start of its cycle to express its full potential right up to harvest.
Managing nitrogen fertilization depends on the previous crop. In the case of cereals, 40 units of nitrogen per hectare must be applied at sowing. It is strongly recommended to apply this fertilizer locally. No additional nitrogen should be applied during vegetation. Excessive nitrogen applications could lengthen the vegetative phase of camelina, delaying maturity.
Where peas are grown before camelina, the nitrogen residue is generally sufficient to ensure good camelina development. Therefore, nitrogen is not essential. However, an optional fertilization of 10 units of nitrogen per hectare at sowing can be considered.
No background fertilization is required.

Camelina editions
Our other articles
Réglette azote colza® (Rape nitrogen chart)
The tool calculates the amount of nitrogen to be applied per hectare, and displays additional recommendations for application.











