Excessive winter rainfall penalizes crop recovery
The wet, rainy conditions at the end of winter, which this year follow a winter period marked by significant melting of rapeseed in the South-West following episodes of cold and frost, are slowing down or even penalizing the crop's recovery in two ways: a lack of practicability of the plots, preventing nitrogen and sulfur inputs, and excess water that can cause asphyxia or even fermentation of the root system.
The wet, rainy conditions at the end of winter, which this year follow a winter period marked by significant melting of rapeseed in the South-West following episodes of cold and frost, are slowing down or even penalizing the crop's recovery on two counts: a lack of practicability of plots, preventing nitrogen and sulfur inputs, and excess water that can cause asphyxia or even fermentation of the root system. This raises the question of the fertilization strategy to adopt for late returns to the field and, in certain situations (flooded valley bottom plots, hydromorphic soils, low-filtering plains, etc.), the maintenance of certain plots.
Adapting fertilization practices to the condition of the colza at harvest time
Reduce the total nitrogen dose only in plots severely affected by excess water.
In most situations, the colza plants were well established and developed at the start of winter. Although excess water over the past few weeks has prevented the application of nitrogen at the start of vegetation, the condition of the colza (deep roots, high autumn biomass) is not a limiting factor for an unhindered recovery. In this context, the forecast spring nitrogen doses can be maintained. The only question is how to divide up the doses.
On the other hand, for plots where excess water stagnates on the surface (lower slopes, flooded or saturated non-drained plains, hydromorphic soils), penalizing the recovery of colza, it is important to adapt the fertilization strategy on a case-by-case basis:
For plots that were initially poorly developed in autumn (poor planting, early pest damage, etc.) and faced with significant excess water, we may consider lowering their yield potential, and by extension the total dose to be applied in spring. Oilseed rape crops with poorly developed root systems in autumn and damaged by excess water will be less able to compensate for biotic stress (pest attacks, disease, soiling) and abiotic stress (water stress) in spring. To avoid making investments that will probably not pay off at harvest, it is advisable to control operating costs as much as possible, especially fertilizer costs, which are generally the heaviest for the crop.
For plots where the rapeseed has been well established (homogeneous, dense stand, low soil contamination, high biomass in autumn, little pest damage), it is advisable to monitor its progress over the next few days. The likelihood of a smooth recovery is much greater, which means that, barring exceptional circumstances, it is not necessary to revise the forecast doses downwards.
Fractionate inputs to support the recovery and guarantee nitrogen nutrition right up to flowering
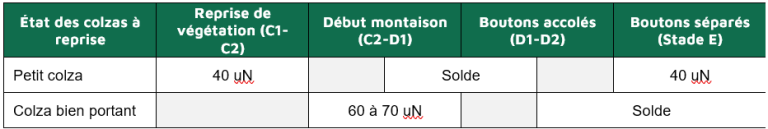
As soon as plots are ready for use again, and if weather conditions are favorable, we recommend adapting the 3-spray nitrogen strategy for the weakest colza plants, with a moderate first spray of 30 to 40 uN to enable the plant to support its growth. A final application of 40 NU should be reserved for the E stage (separated buds). The remainder can be applied at stages D1-D2 (buds together). In this case, there's no point in supporting the recovery with a substantial input from the outset, as the rapeseed's absorption capacity is limited!
For the most healthy rapeseed (> 1 kg/m² at winter's end) and/or well-established plants already at C2 (visible internodes) or even D1 stage, an initial application of around 60-70 uN should be made when the plots are passable. There's no need to hurry with these colza crops, whose good rooting guarantees a good capacity to absorb nitrogen from the soil. The balance can be applied between the D2 and E stages.
Don't forget sulfur
Rapeseed is a very demanding crop in terms of sulfur. The risk of deficiency is much greater in difficult years, when there is a lot of excess water in the autumn and at the end of winter. Consequently, we must not neglect sulfur fertilization of the crop, preferably with sulfate fertilizers (ammonium sulfate, sulfur ammonium nitrate, etc.) for a total of 75 units to be applied at the beginning of bolting (Stages C2-D1).
A reminder of the effects of excess water on rapeseed metabolism
In certain situations (hydromorphic soils, flooded plots, saturated soils with poor filtration, poorly established and/or poorly developed fall rape crops) where rape crops are "completely at a standstill", the question of turning over and replacing the crop may arise. Here are a few reminders about the effect of excess water on rapeseed activity, and the importance of making a detailed diagnosis of the plots concerned before making any decisions.
Excessive water can affect the metabolic activity of oilseed rape on two levels:
Root asphyxia
When soil oxygen levels fall below 10%, nitrogen uptake is blocked, penalizing nitrogen nutrition and, by extension, plant growth.
Fermentation of the root system
In the prolonged presence of water, rapeseed roots ferment, leading to an accumulation of ethanol in the leaves. As ethanol accumulates, photosynthesis, and by extension growth, is affected (the leaf takes on a brown to red color). If the accumulation becomes too great, foot loss is observed.
Aggravating factors
These phenomena are exacerbated by low biomass levels at winter's end, combined with poor plant establishment (rooting depth 15 cm, "forked" or "bent" pivots), the origin of which is soil structure problems, and sometimes basic fertilization. Soiling and autumn pest damage (flea beetle larvae and/or terminal bud weevils) are also factors limiting the compensation and recovery capacity of oilseed rape crops, particularly when they are underdeveloped in autumn.
So, depending on the growth and development dynamics of the rapeseed in autumn, its rooting quality, the state of soiling of the plot, the damage caused by autumn pests and the speed at which the soil dries out, the effects of excess water on recovery capacity, and by extension on yield potential, can be very different from one plot to another.
Maintain or turn over? A decision not to be taken lightly!
In certain situations where the colza does not seem to be recovering, the question arises as to whether the plot should be maintained or turned over. While the decision is straightforward in extreme cases (where the plot is intact or, on the contrary, shows heavy root necrosis), it is much more delicate in intermediate situations, depending on the percentage of the plot concerned and, above all, the evolution of the symptoms.
Diagnose each plot carefully to determine whether it should be maintained
First of all, it's important to assess the impact of turning the plot over in relation to maintaining the crop: the investment already made, regulatory aspects, the potential and feasibility of the replacement crop, depending on the herbicides used.
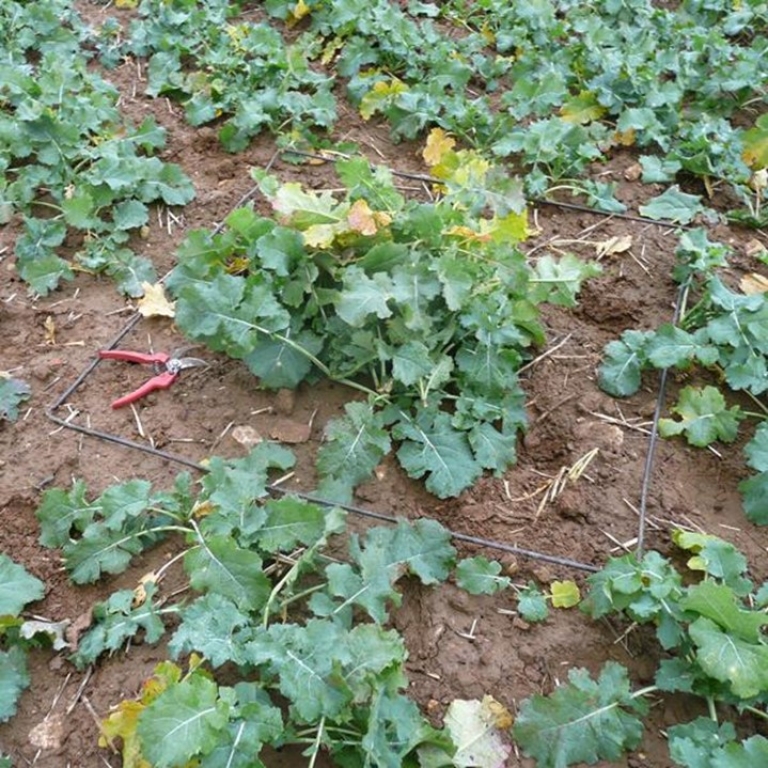
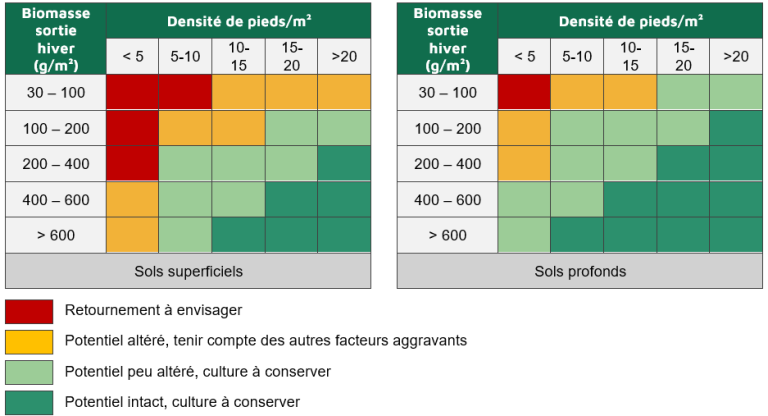
To assess the relevance of turning over a plot, you need to estimate the rapeseed's capacity to compensate, its fresh biomass (green weight expressed per m²) and the density of the stand, as well as any aggravating factors (hydromorphy, weediness, poor rooting, pest damage, heterogeneous stand, etc.). There's no point in leaving poor colza in plots that are likely to get dirty quickly in spring, and whose yield potential is very limited.
Here are a few points of reference to help you decide whether or not to keep plots where suspicions persist:
1. Plant stand
Depending on soil type, from 5 to 10 healthy, well-distributed plants/m², with controlled weediness, turning over the plot is not recommended.
2. Root health
To observe root necrosis, roots must be taken and cut longitudinally to identify the affected areas. If root necrosis is too severe, the plant's survival is seriously compromised. Depending on climatic conditions (particularly the return of a rainy period), necrosis may evolve. It is therefore advisable to regularly check the progress or stagnation of necroses in lightly to moderately impacted plots to confirm the diagnosis.
| Longitudinal section of a healthy rapeseed root | Longitudinal section of a necrotic rapeseed root |

| 
|
3. Percentage of plot affected by damage
In order to consider turning, the surface area affected by heavy necrosis must be sufficient to justify new expenses (operating costs and passage costs). If the surface area affected represents only a few percent of the plot, the decision will be made to maintain the crop in the area, but it will be necessary to be vigilant about weed infestation at the end of the cycle, particularly grass infestation. Weed management should be considered during intercropping and in the following crop.
4. Level of infestation with flea beetle larvae or terminal bud weevils
This is an aggravating factor in the presence of root necrosis.
In all cases, the stress tolerance and compensatory capacities of rapeseed in spring are likely to be limited in situations where root systems are damaged by excess water. This must be taken into account when planning spring fertilization!
Replacement crops
When turning over a plot and replacing a crop, it is important to take into account the history of herbicide specialties used in autumn/winter, in order to adapt the choice of species. Click here for a table of possible replacement crops after turning over an oilseed rape plot, depending on the weed control program used.
Your regional contacts
- Quentin LAMBERT (q.lambert@terresinovia.fr) - Regional Development Engineer - Occitanie
- Quentin LEVEL (q.level@terresinovia.fr) - Regional Development Engineer - Ex-Aquitaine, Gers, Hautes-Pyrénées

The 2026 growing guide for sunflowers is now available
Terres Inovia has updated its sunflower growing guide. This comprehensive guide, updated with the institute's new visual identity, will accompany growers and advisors step-by-step through the coming campaign. As in previous years, it can be downloaded free of charge from the Terres Inovia website, or ordered in printed form.
Terres Inovia a mis à jour son guide de culture consacré au tournesol. Ce support complet, actualisé avec la nouvelle identité visuelle de l’institut, accompagnera pas-à-pas les producteurs et les conseillers lors de la prochaine campagne. Comme chaque année, il est téléchargeable gratuitement sur le site internet de Terres Inovia et peut également être commandé en version imprimée.
Économe en intrants et bénéficiant d’un progrès génétique continu, le tournesol est une culture durable et compétitive, pourvoyeuse de bénéfices pour les systèmes de culture dans lesquels il est inclus. Tête de rotation à cycle court, doté d’une bonne capacité de tolérance au stress hydrique, il s’adapte à de nombreux contextes de production.

Le guide de culture tournesol de Terres Inovia permet de tout savoir sur l’itinéraire technique du tournesol : choix variétal, implantation, stratégie de lutte contre les bioagresseurs, conservation des graines, etc.
Dans cette édition 2026, Terres Inovia a actualisé l’ensemble de ses conseils et positions techniques, à l’instar des recommandations pour lutter contre le mildiou, les caractéristiques réglementaires des solutions préconisées, ou encore la liste des variétés évaluées dans le réseau Terres Inovia. Quant aux références économiques présentées, elles sont en phase avec les éléments de contexte actuel.
Le guide en version imprimée est également gratuit, seule une participation aux frais de port est demandée. Le guide de culture tournesol 2026 sera livré à partir du 23 février 2026.

Nos autres actualités
North & East zone - Sunflower crop report 2025
Spécial Tournesol 2026: Tertes Inovia renews its partnership with the Réussir group
Once again, the technical institute has contributed to the preparation of a publication dedicated to sunflower cultivation, published by the Réussir group.
Une nouvelle fois, l'institut technique a contribué à l'élaboration d'un support édité par le groupe Réussir et dédié à la culture du tournesol.
Dans ce nouveau numéro du Spécial Tournesol 2026, plusieurs articles ont été rédigés par les experts de Terres Inovia.
- Une année 2025 chaude, sèche et... peu productive, par Elodie TOURTON.
- Phosphore, potasse : les apports sont-ils bien valorisés ? par Emile LEREBOUR
- Quel intérêt de la fertilisation azotée ? par Emile LEREBOUR
- Évaluer le risque taupin et noctuelle terricole pour adapter la lutte, par Laurent RUCK
- Un verticillium qui gagne du terrain dans l'ouest et le centre de la France, par Cécilia FONTYN
- Dégâts d'oiseaux à la levée : comment diminuer les risques ? par Christophe SAUSSE
- Caractéristiques des variétés de tournesol selon leur type et leur précocité, par Céline MOTARD
Consultez le Spécial Tournesol 2026 : ici.
Emile LEREBOUR - e.lerebour@terresinovia.fr
Laurent RUCK - l.ruck@terresinovia.fr
Cécilia FONTYN - c.fontyn@terresinovia.fr
Christophe SAUSSE - c.sausse@terresinovia.fr
Céline MOTARD - c.motard@terresinovia.fr
Rapeseed: Assessing rapeseed biomass to optimize spring nitrogen fertilization
Raisonner la fertilisation azotée des colzas est indispensable pour assurer la productivité de la parcelle et maîtriser le poste de charge opérationnel le plus important de la culture. L’estimation de la biomasse du colza à la sortie de l’hiver et sa prise en compte dans le calcul de dose d’azote est un moyen simple et efficace pour optimiser sa marge brute.
L’estimation de la biomasse en sortie hiver est indispensable pour ajuster la quantité d’azote à apporter au printemps car la biomasse aérienne (pois vert en kg/m²) est un bon indicateur de l’azote déjà absorbé par la plante. Plus la quantité d’azote absorbé par la culture à l’ouverture du bilan est importante, plus la dose d’azote à apporter sous forme d’engrais au printemps est faible, sans compromis sur le rendement.
L’estimation de la biomasse est à faire lors de la reprise de végétation (stade C1 – C2) et dans tous les cas avant le premier apport d’azote.
Méthode d’estimation de la biomasse par pesée
La pesée s’effectue sur 2 à 4 parcelles d’1 m² en sectionnant les colzas au ras le sol pour une bonne estimation de sa biomasse aérienne. La méthode de prélèvement varie selon l’écartement du colza (voir tableau ci-contre).
Ecartement | Méthode de prélèvement |
Inférieur à 30 cm | Prélever dans un carré de 1 mètre de côté |
45 cm | Prélever 2 rangs contigus de 1,10 mètre linéaire |
50 cm | Prélever 2 rangs contigus de 1 mètre linéaire |
Dans les parcelles avec des colzas hétérogènes, il est recommandé de réaliser 4 prélèvements, à différents endroits représentatifs de la parcelle, tout en évitant les bordures. La valeur moyenne sera alors retenue pour effectuer les calculs de dose d’azote.
Pour éviter tout biais de mesure, notamment en cas de prélèvement par temps pluvieux ou en cas de forte rosée, il convient de bien secouer les plantes pour les débarrasser des gouttes d’eau, de retirer les feuilles blanches en décomposition gorgées d’eau et d’enlever les éventuelles mottes de terre et autres débris.
D'autres outils pour estimer la biomasse des colzas
Il existe aujourd’hui une grande diversité d’opérateurs proposant des services de conseils azoté spécialisés sur le colza à partir d’un traitement d’image. Ils permettent aux agriculteurs qui le souhaitent de moduler les apports au sein de la parcelle, soit avec un système piloté sur l'épandeur d'engrais, soit en modulant manuellement par grandes zones dans les parcelles présentant des états de croissance différents. Parmi eux, 4 produits font l’objet d’un accord de partenariat avec Terres Inovia :
- Farmstar (Airbus, Arvalis)
- Agro-rendement (Wanaka/Agroptimize - Geosys)
- PRECIFert Azote (Precifield)
- Bilan Colza by Abelio (Abelio)
Pour faciliter les estimations au champ, 2 applications smartphone, ImageIT inclus aujourd’hui dans Atfarm (Yara France) et Crop-Analyser (Visio-Crop), font l’objet de partenariat avec Terres Inovia. La biomasse est estimée à partir de photographies classiques, dont l'exploitation et l’interprétation sont ajustées par la hauteur de végétation, à renseigner en amont du traitement d’image.
Pour aller plus loin : Evaluer la biomasse du colza pour optimiser les apports d'azote au printemps
Calcul de la dose prévisionnelle : attention à la surestimation des besoins !
La Réglette azote colza® - outil simple, facile d’utilisation et mis en ligne gratuitement par Terres Inovia - détermine la dose totale à apporter à partir de plusieurs informations : la biomasse du colza, l’objectif de rendement de la parcelle, le type de sol, l’apport de produits organiques, la nature du précédent et éventuellement l’association de légumineuses gélives.
Afin de ne pas surestimer les besoins de la culture, et ainsi éviter une sur-fertilisation inutile et coûteuse dans un contexte de prix élevé des engrais azotés, il convient de fixer un objectif de rendement raisonnable : calculer la moyenne des rendements des 5 derniers colzas sur la parcelle ou des parcelles comparables, en enlevant la valeur la plus faible et la valeur la plus élevée (moyenne olympique).
Fractionner pour synchroniser les apports aux besoins de la culture
Pour les colzas à faible croissance, un premier apport précoce dès la reprise de végétation, en petite quantité, est recommandé. Il est en effet nécessaire d’accompagner la reprise car les petites plantes ont peu de réserves et une capacité d’absorption limitée.
Pour les colzas à forte croissance, la remobilisation des réserves accumulées dans les organes suffira à assurer une bonne reprise de végétation. Il est conseillé d’attendre la montaison pour l’apport éventuel d’azote.
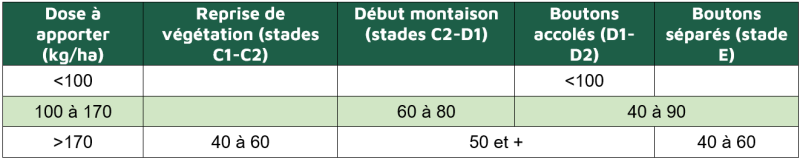
Dans tous les cas, ne pas apporter plus de 100 kg/ha d’azote en une fois.
Dose à apporter (kg/ha) | Reprise de végétation (stades C1-C2) | Début montaison (stades C2-D1) | Boutons accolés (D1-D2) | Boutons séparés (stade E) |
<100 |
|
| <100 |
|
100 à 170 |
| 60 à 80 | 40 à 90 | |
>170 | 40 à 60 | 50 et + | 40 à 60 | |
Aurore BAILLET (a.baillet@terresinovia.fr)
Measure your biomass at the end of winter to optimize your nitrogen inputs in spring
Conditions at the start of the campaign enabled good overall development of rapeseed crops, where these did not suffer from poor planting conditions. In order to estimate the amount of nitrogen to be applied in the spring, it is important to measure the biomass of the rapeseed at the beginning and at the end of the winter.
Conditions at the start of the campaign enabled good overall development of rapeseed crops, where these did not suffer from poor planting conditions. In order to estimate the amount of nitrogen to be applied in the spring, it is important to measure the biomass of the rapeseed at the beginning and at the end of the winter.
Weighing in at the end of winter
The rise in temperatures over the past week will enable the colza plants to start growing again, after a vegetative rest and a melting of biomass at the start of winter, following successive drops in temperature between late November and early January. It's now time to start weighing the colza plants, in order to determine the quantities of nitrogen to be applied before and/or during bolting, depending on the situation.
Biomass estimation method
Weighing is carried out on 2 to 4 1m² plots, cutting the colza at ground level for a good estimate of its above-ground biomass. The sampling method varies according to rapeseed spacing (see table opposite).
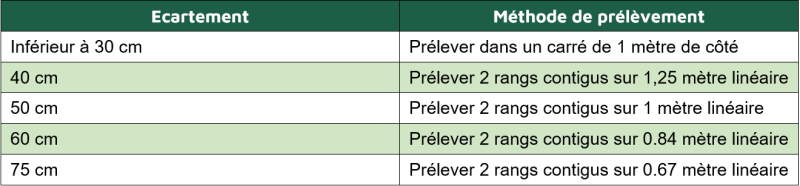
In plots with heterogeneous rapeseed, it is recommended to take 4 samples, at different representative locations in the plot, avoiding the edges. The average value will then be used to calculate the forecast dose.
To avoid any measurement bias, particularly when sampling in rainy weather or heavy dew, it is advisable to shake the plants well to remove any drops of water from the leaves and any clumps of earth from the base of the stem.
To help you
Take a look at this tutorial
Other tools to calculate nitrogen doses directly
Today, there is a wide range of operators offering spatialized nitrogen advisory services for rapeseed, based on image processing. They enable farmers who so wish to modulate inputs within the plot, either with a system controlled on the fertilizer spreader, or by modulating manually by large zones in plots presenting different states of growth. Among them, 4 products are the subject of a partnership agreement with Terres Inovia:
- Farmstar (Airbus, Arvalis)
- Agro-rendement (Wanaka/Agroptimize - Geosys)
- PRECIFert Azote (Precifield)
- Rapeseed Balance Sheet by Abelio (Abelio)
To facilitate field estimates, 2 smartphone applications, ImageIT (Yara France) and Crop-Analyser (Visio-Crop), are partnered with Terres Inovia. Biomass is estimated from conventional photographs, whose processing and interpretation are adjusted by the height of vegetation, to be entered before image processing.
For more information on alternative methods for estimating biomass and forecasting nitrogen doses for rapeseed , click here.
Calculating the forecast dose: Beware of overestimating requirements!
The Réglette azote colza® can be used to determine the total dose to be applied, based on a number of factors: rapeseed biomass, yield objective for the plot, soil type, organic fertilizer application, type of previous crop and, if applicable, the use of gelatinous legumes.
In order not to overestimate the crop's needs, and thus avoid unnecessary and costly over-fertilization, particularly in a context of high nitrogen fertilizer prices compared to rapeseed sales prices, it is advisable to first set a reasonable yield objective. To do this, calculate the average yield of the last 5 rapeseed crops on the plot or comparable plots, removing the lowest and highest values: this is the Olympic average.
Given the temperature conditions at the start of this winter, rapeseed crops in the South-West have lost more biomass than in previous years, when in some years they never really stopped growing and developing. So, in addition to estimating your yield target, you need to take into account the nitrogen absorbed in the autumn, by estimating biomass at the start of the winter (between 800g and 1.2 kg/m² on average, depending on the plot) or by processing satellite images taken between mid-November and early-December. The risk of not taking into account the nitrogen absorbed in the autumn, when the rapeseed has "melted" over the winter, is also an overestimation of the doses to be applied in the spring, by underestimating the quantities absorbed previously (see examples opposite).
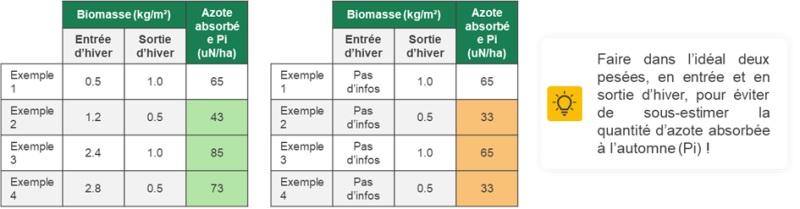
Split your inputs according to the total dose to be applied
By dividing up the doses, you can adjust them to the plant's needs.
For low-growth oilseed rape crops, an early first application is recommended as soon as vegetation starts to grow again, as it is necessary to support the start of vegetation, as small plants have few reserves and cannot easily access nitrogen from the soil due to their weak root system.
On the other hand, for fast-growing rapeseed, it's advisable to wait until bolting before applying nitrogen; the remobilization of reserves accumulated in the plant's organs will be sufficient to ensure good vegetation recovery.
In all cases, do not apply more than 100 kg/ha of nitrogen at any one time.
Your regional contacts :
- Alexandra Denoyelle (a.denoyelle@terresinovia.fr) - Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes & Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur
- Quentin Level (q.level@terresinovia.fr) - Southern New Aquitaine, Gers, Hautes-Pyrénées
- Quentin Lambert (q.lambert@terresinovia.fr)- Occitanie

Mastering camelina cultivation

Our other training courses
Camelina: transforming a diversification crop into a technical and economic opportunity.
Boosted by a rapidly expanding market, camelina requires precise control of its cultivation itinerary if it is to achieve its full potential. This training course offers a complete technical and economic approach to successfully integrating camelina into cropping systems.
The program includes
1. camelina: basics and challenges
- Origin, development cycle and agronomic characteristics
- Crop strengths and positioning in cropping systems
2. market opportunities and value-adding framework
- Main outlets: sustainable fuels, food and feed, cosmetics, industrial uses
- Regulatory context
3.camelina technical itineraries
- Conditions for success and choice of plot
- Planting and varietal selection
- Fertilization and weed management
- Pest and disease management
- Adapting the itinerary to the type of crop: main crop, summer or winter catch crop, intercropping
4 Harvesting and securing production
- Key harvesting principles and settings
- Mowing and raking
5.camelina in organic farming
- Agronomic benefits
- Technical specificities and outlets
6.economic performance
- Comparison of margins according to technical itineraries
- Economic analysis at crop system level
7.field diagnosis
- Observation of plots and/or trials
- Collective analysis of situations encountered
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Understand the agronomic, economic and regulatory issues involved in growing camelina.
- Identify the various outlets for camelina and their requirements
- Recommend key cultivation techniques for successful camelina production, whatever the cropping method (main crop, catch crop, combination, organic farming).
- Adapt camelina technical itineraries to soil and climate conditions and to production objectives.
Face-to-face format with a field component (depending on conditions and training period):
-
Theoretical classroom input: Presentation of the crop, its outlets and technical itineraries (main crop, catch crop, combination), illustrated by trial results and concrete case studies.
-
Field observation: Analysis of real-life situations in plots and observation of trials to carry out collective diagnoses and illustrate technical levers.
Active methods: Presentations, case studies, practical exchanges, questions and answers, applied diagnostics.
Assessment: Quiz to validate knowledge acquired, questions and answers throughout the course, self-assessment by participants, individual satisfaction survey.
Theoretical support: Presentations, lectures, regulatory texts and summary documents given to participants.
Case studies: Real-life situations based on experimental results and feedback from the field, analyzed collectively.
Practical exchanges: Sharing of experiences between participants and trainers to enrich technical analysis and diagnoses.
Technicians, agricultural advisors, farmers, agents of structures working with camelina for biofuel production Q&A, quiz, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioningIf you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the Disability Advisor:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 0€ TTC https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/h17x4yzwmvzfgytkjb6Aq7zA3flf2q6khf1xmsczn8qAw8jpnz5sw4brlfk2kAbynAvwgpj5h35tqtkdkrhg3rtsm7yAyrjA4rzs9vlhjr7g4pj8 1 Jour 102 Intra-entrepriseAgronomic control of chickpea and lentil cultivation in the southwest of France
Our other training courses
Integrating lentils and chickpeas into your crop rotations: a strategic agronomic choice
Lentils and chickpeas are economical, high-performance crops that improve soil fertility, break pest and disease cycles and offer secure outlets. Adapted to the pedoclimatic context of the South-West of France, the training course offers theoretical contributions and visits to master technical itineraries and integrate these legumes sustainably.
Program:
1 Introduction to legumes:
- Definition of legumes and how they work,
- Role of legumes in soil fertilization and crop rotation.
2 - Lentil management in the South-West of France
- Agronomic characteristics: spring species, low-input crop
- Typologies (blond, coral, green) and value-adding opportunities
- Adapting the technical itinerary to regional constraints: soil types, water availability, temperatures, etc.
- Planting, varietal selection, cultural management, fertilization, protection
- Harvesting: optimal conditions, equipment settings
3. chickpea management in the South-West
- Agronomic, environmental and economic benefits
- Regionalized technical itinerary: choice of sowing dates, densities, management in dry conditions, harvesting, storage and contracting.
- Management of pests and diseases specific to the region
4 Focus on organic farming
Training carried out in collaboration with FILEG (free for their members)
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Explain the agronomic functioning of lentil and chickpea crops
- Identify their agronomic, economic and environmental benefits
- Choose species and varieties suited to the soil and climate conditions of the South West of France
- Implement rational crop management: planting, fertilization, weed and pest management
- Diagnose the main crop accidents
- Apply good harvesting and post-harvest practices
- Integrate the specificities of organic farming into the local context
Face-to-face format:
-
In-class technical input: presentations, case studies, interactive discussions
-
Practical application in the field: plot visits, crop observation, etc.
Active methods: Illustrated presentations, debates, questions and answers, feedback
Evaluation: Quizzes, questions and answers, application exercises, individual satisfaction surveys, self-assessment
Theoretical support: Lectures, visual presentations, written material given to participants.
Field visits: Analysis of lentil and chickpea crops in real-life conditions, identification of key technical points.
Practical exchanges: Feedback from field experience and group discussions with the trainer.
Advisors/Technicians from development, economic and agri-supply organizations. Teachers. Farmers Quiz, Q&A, application exercise, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioningIf you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 480€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/nf6fsAsf4852qmjwlj3gqzsjgv6g97l3mn2x4ml2nbgwsAlx4flhkmk5mjww49tc3nbggpj5hjlw2765g8lhgyzA3fgAc9trjf8hmq5kmfbAcpj8 1 Jour Quentin LAMBERT 94 Inter-company and intra-companyGrowing soybeans successfully in the South-West
Our other training courses
Soya, a crop of the future to be mastered!
In a context of agro-ecological transition, soybeans are back in the spotlight thanks to their low input requirements and varied outlets. Boosted by regulatory and economic support (protein plan, MAEC, SIE...), this crop offers real opportunities in both conventional and organic farming. This training course will provide you with a comprehensive, practical technical approach to successfully manage each stage of the crop, secure your yields and make the most of your production.
The program includes
1 Plant and canopy functioning:
- Key aspects of soybean physiology and phenology
- Highlighting levers for improving yields
2 - Cultural management adapted to the South-West :
- Planting
- Weed management
- Crop protection
- Water management
- Harvest control
3 Diagnosis of major accidents :
- Recognition of soybean pests
- Identification of root and leaf diseases
- Frequent climatic accidents in the South West
4 Approach to organic crop management
5 - Soybeans in catch crops: some indicators
Training organized in collaboration with FILEG (free for their members)
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Understand how plants function
- Analyze the factors influencing yield and the technical levers for optimization
- Recommend key cultivation techniques for successful soybean cultivation
- Implement good harvesting practices
- Detect and diagnose major crop failures (pests, diseases, abiotic stresses)
- Adapt crop management to the specificities of organic agriculture
Face-to-face format (1 day) :
-
Theoretical input via illustrated presentations and case studies.
-
Interactive exchanges between participants and trainers to share experiences and questions.
Active methods: Presentations, case studies, debates, questions and answers.
Evaluation: Quiz, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.
Theoretical support: Lectures, presentations, written material given to participants.
Case studies: Feedback from the field to illustrate best practices and solutions.
Exchange of practices: Discussions and sharing between trainees and trainers.
Agricultural technicians and advisors, Farmers and producers, Agricultural teachers and trainers, Agronomic and technical sales managers in agricultural distribution, Agri-food / processing industry players Quiz, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioning.If you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 480€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/jv72wsdgmr5hgzdf4ztwyrdxmngvm7dw4brh16cxj27A2wrr38rcwz53hbfgy5lmmzt25pj5hj6x1Azrj77v46cnn83w99jvgngs98bvgzhfcpj8 1 Jour Quentin LAMBERT 93 Inter-company and intra-companyHemp: a high-potential crop that requires careful management
Our other training courses
A no-input crop requiring limited fertilization, hemp responds particularly well to the mastery of basic production techniques. The expansion of outlets (construction, automotive, textiles, human food) makes hemp a crop with interesting development potential. In terms of surface area, France is currently the world's 2nd largest producer.
Program:
- Presentation of the hemp industry: history, players and organization of the sector
- Hemp outlets: Main value-added sectors (textiles, construction, food, etc.)
- Hemp physiology: Understanding the key biological elements for optimized cultivation, and adaptability to climate change.
- Specificities of hemp cultivation: Adaptation to soils, choice of varieties, water and nutrient requirements.
- Harvesting techniques: methods and equipment for efficient hemp harvesting
- Identifying the main phytosanitary problems: Damage observed on the crop and prevention strategies
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Explain the organization of the hemp industry and its various stages of development
- Analyze the agronomic, economic and environmental issues involved in growing hemp
- Identify and recommend the key cultivation techniques for successful hemp cultivation for different outlets.
Theoretical presentations in the classroom: clear, concise presentations on the hemp industry, its challenges, cultivation techniques and outlets.
Discussions and debates: time for interaction between participants and the trainer to share experiences, ask questions and explore key points in greater depth.
Plot visits: hands-on observation of cultivation techniques, varieties, development stages and any phytosanitary problems.
Interactive approach: the trainer, hemp expert Louis Marie ALLARD, leads the session in a dynamic way, drawing on feedback and case studies.
Evaluation: End-of-session quiz, questions and answers, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.
Visual aids: illustrated presentations (diagrams, photos, graphs) to facilitate understanding of technical and economic concepts.
Pedagogical documents: handing out synthetic aids (data sheets, guides, memos) to enable participants to keep a written record of key information.
Knowledge acquisition tests: quizzes or questions and answers to assess participants' understanding and reinforce important points.
Plot visits: direct observation of crops, soils, varieties and cultivation practices, for hands-on immersion.
Development technicians, agri-supply and distribution professionals, teachers, farmers. End-of-session quiz, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioningIf you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 240€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/nntw98djkrbAcrl5pjxw46kbmfywgsk4mzsdmzlr3qzxcq5d475hm9brkjh279tymzkAspj5hj3v3slvknA2c9rw3zlv3yjtn3xAcmkAkf5h4pj8 1 Jour Louis-Marie ALLARD 50 Inter-company and intra-companyMastering sunflower cultivation
Our other training courses
A sustainable, competitive crop that provides ecosystem benefits, sunflower needs to be managed carefully to achieve its full potential. This training course provides you with the technical keys and agronomic benchmarks you need to secure your itineraries and maximize field performance.
Program:
- Plant physiology: the key stages in sunflower development, and the main abiotic factors influencing yield.
- Crop management: intercropping, planting, fertilization, weed control (including post-emergence), plant protection, irrigation, harvesting
- Analysis and management of crop accidents: identification, causes, means of action
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- recommend the key cultivation techniques for a successful technical itinerary in sunflower
- diagnose major accidents that may occur during the crop cycle
Hybrid format:
-
Remote theory (2 hours): Technical inputs, case studies, interactive quizzes via Teams.
-
Field practice (1 day): Analysis of plots, observation of development stages, diagnosis of crop accidents, exchanges with the trainer.
Active methods: Presentations, discussions, debates, questions and answers, case studies, field diagnostics.
Evaluation: Quiz, oral questions and answers, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment at start and end of training.
Theoretical support: Lectures, presentations, written material given to participants.
Management tools: Presentation of technical levers for adapting cropping itineraries to specific contexts.
Field visits: Observation and diagnosis in the field to analyze development stages and crop accidents.
Practical exchanges: Feedback, discussions and debates between participants and trainer to enhance learning.
Technicians from development, agri-supply and distribution organizations. Farmers. Teachers. Quizzes, oral questions and answers, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment at the beginning and end of the courseIf you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 700€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/jzldgwbA4zzf2qkx3v7t2ztqk8qA3Akqmjcdcyl44y7Am6syljsgyAjwjj5vsqldfn5vkpj5hjtgq9trgjjt2wcllfvtqr5qpjcvmAdmkn5h4pj8 2 Jours 49 Inter-company and intra-company