Automatically generated translation
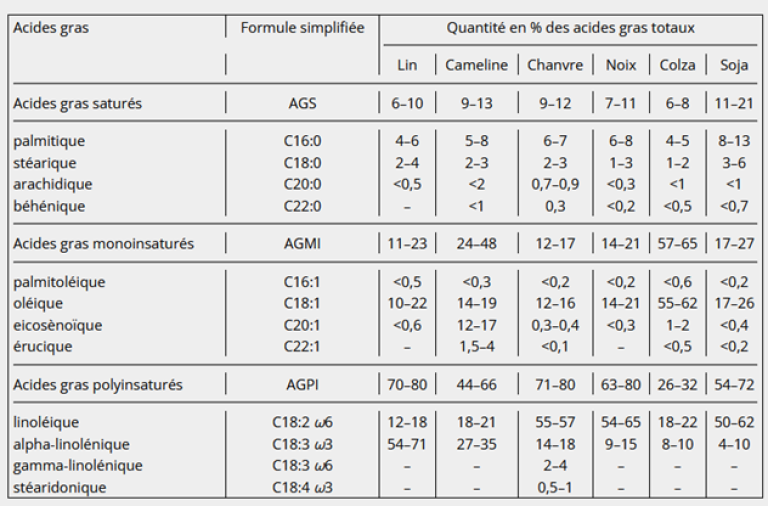
Camelina is an oilseed crop whose seeds are characterized by an original fatty acid profile and high protein content. These properties make it ideal for a wide range of uses.
To date, its main uses have been in the production of oil for human consumption and the recovery of oilcake for animal feed. However, there is growing interest in applications in cosmetics, green chemistry and the formulation of technical specialties. What's more, a French industry is currently developing around camelina grown in intercropping, specifically geared towards the production of sustainable aviation fuels.
| Oil content (%MS) | 28-49% |
| Of which a-linolenic (ω-3 precursor) | 28-50% |
| Of which linoleic (ω-6 precursor) | 15-23% |
| Ratio ω-3/ω-6 | 1.3-2.6 |
| Protein (% DM) | 24.1-35.7% |
A new chain for the production of sustainable aviation fuels
A particularity of camelina is its short cycle - the camelina cycle can be completed in around 3 months - which makes it ideal for intercropping.
Furthermore, to decarbonize the aviation sector as part of the implementation of the European climate law, the European Union adopted the RefuelEU Aviation regulation in 2024. This regulation sets significant targets for the incorporation of biofuels by 2050.
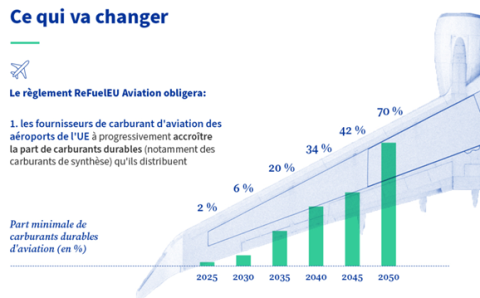
Moreover, recent developments in the Renewable Energy Directive II (RED II) have classified intercrop feedstocks as "advanced biofuels"(Annex 9A of RED II), making them eligible for the production ofaviation biofuel.
Thus, intercrop crops such as camelina represent one of the ways of achieving the objectives of integrating biofuels into aviation, which suggests that there will be considerable demand for them in the years to come.
What's more, camelina's low input requirements make it possible to adopt a technical itinerary with low greenhouse gas emissions, a necessity for its conversion into biofuel. Saipol, a subsidiary of the Avril Group, is working on the development of a camelina production chain based on intercropping.
Human food
Camelina oil belongs to the family of oils rich in omega-3 fatty acids, behind flax but ahead of hemp, walnut and rapeseed. Thanks to its high omega-3 content and optimal ω-3/ω-6 ratio, it offers interesting nutritional qualities for rebalancing our diets, which are currently too rich in omega-6 compared to omega-3.
What's more, its richness in antioxidants such as vitamin E ensures good stability and limits oxidation, compared with other omega-3-rich oils. It is mainly consumed for seasoning, but can also be used in the formulation of dietary supplements (authorized in 2019 by the Direction Générale de la Concurrence, de la Consommation et de la Répression des Fraudes - DGCCRF).
Figure 2. fatty acid compositions of flax and hemp oils compared with those of other vegetable oils in the alpha-linolenic family (camelina, walnut, rapeseed and soybean). Morin et al. 2015, OCL
The human food market currently mainly concerns organically produced camelina, and remains a relatively undeveloped market.
Cosmetics
Camelina oil is also used in the formulation of cosmetic products, notably for its high antioxidant content.
Other outlets
Research and industry are exploring a variety of applications for camelina oil and meal, such as the formulation of bioplastics, adhesive agents, biopesticides, bioherbicides, biostimulants, etc. The Carina project, for example, is exploring the valorization of camelina and Abyssinian mustard (brassicata carinata) for the formulation of biopesticides and biostimulants.
Animal feed
Camelina meal has a high protein content of around 45%, making it an interesting ingredient to include in animal feed rations.