Automatically generated translation
Adapted to a wide range of soil and climate conditions, camelina is grown throughout France. It can be easily integrated into a variety of cropping systems, in both conventional and organic farming.
A particularity of camelina is its very short cycle length, which also makes it suitable for intercropping.
Camelina as the main crop
Pure cultivation
Camelina can be grown pure as a main crop, with winter and spring varieties. In areas with mild climates (winter temperatures not exceeding -10°C), spring varieties can also be planted in autumn.
As a main crop, the proportion of organically-produced camelina is particularly high, thanks to its hardiness and resistance to pests and diseases, and to the opportunities for using the oil for human consumption.
In some countries of the southern Mediterranean basin, camelina is grown on so-called "marginal" land with low potential, which it valorizes well.
In combination
Camelina lends itself well to crop combinations, particularly in organic farming. The lentil-camel association is widely practiced, with camelina acting as a staking plant, thus limiting the risk of lentil lodging.
What's more, if planting conditions are favorable, camelina develops rapidly and is highly competitive with weeds at the rosette stage, in contrast to the generally slow initial development of legumes, which contributes to better weed control. Other camelina-legume combinations mentioned in the literature are camelina combined with pea, lupin or chickpea.
There are also references to camelina combined with barley or wheat, but these refer to competition between the two species and associated yield losses (M. Leclère's thesis on camelina insertion in Picardie).
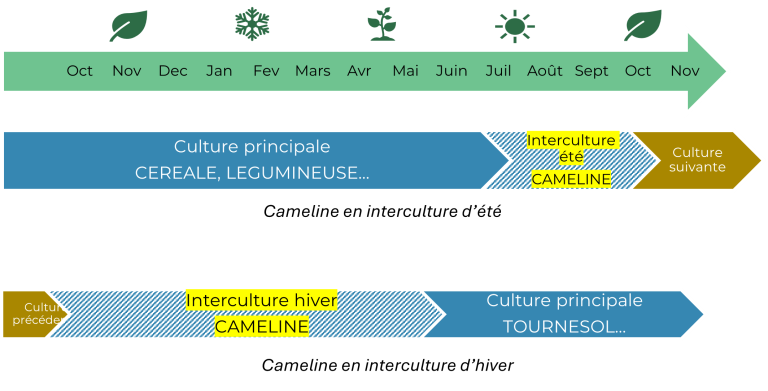
Intercropping
The length of camelina's cycle, around 3 months for short-cycle varieties, means that it can be grown as a catch crop. Recent changes in the regulatory framework open up major market opportunities for intercropped camelina, such as sustainable fuel for aviation.
Summer intercropping
While camelina adapts well to a wide range of soil and climate conditions, a number of conditions must be met to maximize its chances of success in summer intercropping: sufficient rainfall during the planting period (late June - early July), few days of high temperature (35°C - 40°C) during flowering, and a sufficient temperature sum (1700°J base 0) to reach maturity before mid-October. These criteria exclude areas very far north and south of France.
To maximize the chances of success, camelina in summer intercropping should be planted after an early-harvested preceding crop, such as barley or winter peas.
Winter intercropping
Camelina can also be intercropped in winter, before a late-sown spring crop such as sunflower or sorghum. The challenge for this type of succession is to harvest the camelina early enough, so as not to delay the sowing of the following crop too much and impact its yield potential.