The 2026 growing guide for sunflowers is now available
Terres Inovia has updated its sunflower growing guide. This comprehensive guide, updated with the institute's new visual identity, will accompany growers and advisors step-by-step through the coming campaign. As in previous years, it can be downloaded free of charge from the Terres Inovia website, or ordered in printed form.
Terres Inovia a mis à jour son guide de culture consacré au tournesol. Ce support complet, actualisé avec la nouvelle identité visuelle de l’institut, accompagnera pas-à-pas les producteurs et les conseillers lors de la prochaine campagne. Comme chaque année, il est téléchargeable gratuitement sur le site internet de Terres Inovia et peut également être commandé en version imprimée.
Économe en intrants et bénéficiant d’un progrès génétique continu, le tournesol est une culture durable et compétitive, pourvoyeuse de bénéfices pour les systèmes de culture dans lesquels il est inclus. Tête de rotation à cycle court, doté d’une bonne capacité de tolérance au stress hydrique, il s’adapte à de nombreux contextes de production.

Le guide de culture tournesol de Terres Inovia permet de tout savoir sur l’itinéraire technique du tournesol : choix variétal, implantation, stratégie de lutte contre les bioagresseurs, conservation des graines, etc.
Dans cette édition 2026, Terres Inovia a actualisé l’ensemble de ses conseils et positions techniques, à l’instar des recommandations pour lutter contre le mildiou, les caractéristiques réglementaires des solutions préconisées, ou encore la liste des variétés évaluées dans le réseau Terres Inovia. Quant aux références économiques présentées, elles sont en phase avec les éléments de contexte actuel.
Le guide en version imprimée est également gratuit, seule une participation aux frais de port est demandée. Le guide de culture tournesol 2026 sera livré à partir du 23 février 2026.

Nos autres actualités
North & East zone - Sunflower crop report 2025
Winter beans: Intense and early disease pressure as soon as winter emerges
The wet and relatively mild conditions of January were favorable to the early and rapid development of leaf diseases in winter faba bean crops in the South-West of France, mainly Botrytis, but also Ascochytosis (formerly Anthracnose) to a lesser extent. In the most severe cases, and in situations where destruction was not initially planned, the question may arise of maintaining the plot and choosing a replacement crop.
The wet and relatively mild conditions of January were favorable to the early and rapid development of leaf diseases in winter faba bean crops in the South-West of France, mainly Botrytis, but also Ascochytosis (formerly Anthracnose) to a lesser extent. In the most severe cases, and in situations where destruction was not initially planned, the question may arise of maintaining the plot and choosing a replacement crop.
A few reminders about disease recognition
Botrytis

Botrytis is a very common aerial disease of winter beans, caused by the fungus Botrytis fabae. Symptoms are evenly distributed throughout the plot, and take the form of numerous small brown spots that spread and merge as the disease develops. Eventually, the disease causes defoliation and flower blight. It appears particularly in early and/or densely-sown plots.
Weather conditions at the start of the year were particularly favorable to the development of the disease, especially on plots sown early (mid-October) and/or in valley bottoms heavily exposed to recent excess water. The first symptoms are also visible on plots sown later (during November). In these circumstances, the risk of damage is already very high.
(Area of Auch (32) on 02/02/2026 - Photo credit: Terres Inovia)
Ascochytose:

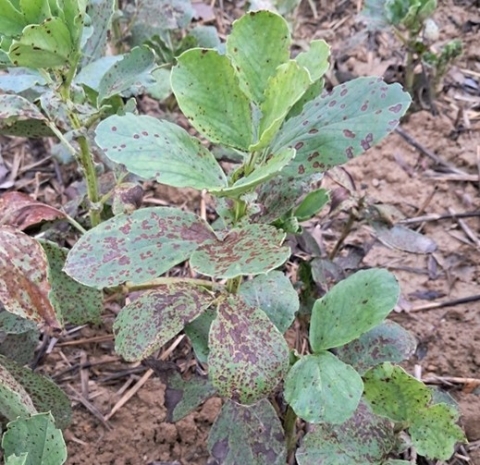
Bien moins fréquente que le Botrytis, l’Ascochytose, anciennement appelée Anthracnose, est provoquée par le champignon Ascochyta fabae. Lorsque les températures sont fraîches (10-15°C) et l’humidité est élevée, elle apparaît en foyers dans la parcelle, caractérisée par des taches brun cendré peu nombreuses avec des points noirs au centre (pycnides). Elles évoluent le plus souvent en « coulures » au pourtour brun-noir. Avec le temps, le centre des taches s’éclaircit et se nécrose allant parfois jusqu’à trouer les feuilles. Sur les tiges, des lésions du même type mais plus allongées peuvent se développer et provoquer des cassures.
Cette maladie est notamment transmise par la semence. Pour limiter au maximum l’inoculum primaire, l’utilisation de semences saines et le traitement des semences sont primordiaux. Le traitement de semences PREPPER (Fludioxonil) est disponible et donné efficace contre l’Ascochytose, mais il n’a pas été évalué contre ce pathogène par Terres Inovia à ce jour.
La majorité des variétés de féverole d’hiver présente un bon comportement vis-à-vis de cette maladie.
(Ascochytose sur féverole d’hiver - Crédit photo : Terres Inovia)
La Cercosporiose

La Cercosporiose (Cercospora zonata) provoque des lésions sombres avec une zonation concentrique sans ponctuations noires. Elles apparaissent précocement à la base du couvert et évoluent généralement peu. Cette maladie est peu fréquente et peu nuisible.
(Rouille sur féverole d’hiver - Crédit photo : Terres Inovia)
La Rouille

La rouille (Uromyces fabae) est une maladie fréquente et très préjudiciable sur féverole. Elle se développe sur le feuillage sous la forme de pustules brun-rouge auréolées d’un anneau plus clair. Lorsque les conditions climatiques sont très favorables (temps chaud >20°C et humide) la rouille peut recouvrir, parfois de manière rapide et fulgurante, la totalité des feuilles voire des tiges, provoquant un dessèchement prématuré des plantes.
Elle peut entraîner jusqu’à 50 % de pertes de rendement (25 à 40 q/ha) lorsque l’attaque est précoce et importante, et qu’aucun traitement n’est réalisé.
(Rouille sur féverole d’hiver - Crédit photo : Terres Inovia )
Comment agir si la maladie est déjà présente ?
Aller observer les parcelles pour estimer le risque de forte nuisibilité Botrytis
Dans ce contexte d’arrivée précoce des maladies sur féverole d’hiver, il convient d’aller observer très rapidement les parcelles assolées pour estimer le niveau d’infestation actuel, et par extension la nuisibilité potentielle. Pour ce faire, il sera nécessaire de réaliser les observations suivantes, sur 5 à 8 placettes de 5 pieds représentatives de la parcelle :
- La densité de peuplement (nombre de pieds/m²)
- L’état sanitaire des pieds sur chaque placette (% de surface foliaire avec symptômes de maladie pour ce qui est du Botrytis, présence de taches pour ce qui est de l’Ascochytose)
En fonction de la densité de peuplement et de la part de surface foliaire touchée par le Botrytis, il est possible d’estimer à priori le risque de nuisibilité significative (> 30%) pour le rendement final de la culture. Terres Inovia a élaboré un tableau d’aide à la décision pour savoir où votre parcelle se situe vis-à-vis du risque Botrytis.
Cette estimation est à réaliser dès maintenant dans le Sud-Ouest. L’expérience nous montre qu’il y a une corrélation entre présence de la maladie en sortie d’hiver et nuisibilité pouvant atteindre jusqu’à 30% de potentiel de rendement à la récolte.
Intervenir lorsque les conditions seront propices ou retourner la parcelle ?
Pour ce qui est du Botrytis, les interventions fongicides n’ont pas d’effet curatif sur la maladie. Du fait de l’impossibilité d’intervenir immédiatement en parcelle, il conviendra de sérieusement penser à procéder au retournement des parcelles déjà fortement infestées (> 15% de surface foliaire avec symptômes dès à présent).
Pour les autres cas, notamment pour les semis tardifs (à partir de la mi-novembre, début décembre), il sera généralement possible de patienter et d’intervenir dès la fin-février ou début mars, lorsque les conditions météorologiques et la portance des sols seront plus favorables. Afin d’adapter au mieux la stratégie fongicide au contexte épidémiologique de l’année, Terres Inovia présente dans son Guide Culture divers exemple de programmes fongicides, qu’il est possible de retrouver ici.
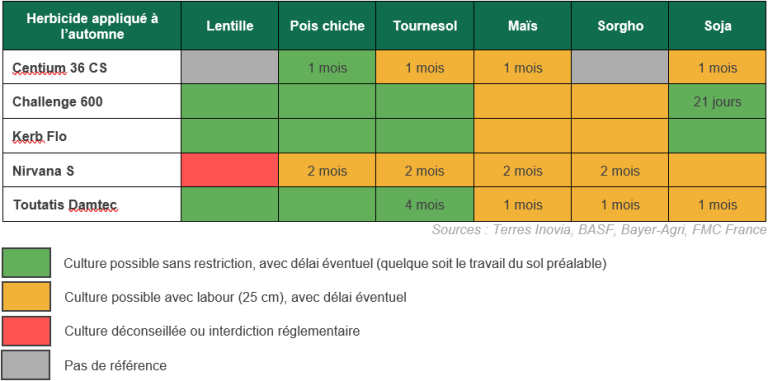
En cas de retournement de la parcelle, le choix de la culture de remplacement dépendra, entre autres, des programmes de désherbage appliqués en entrée d’hiver. Voici un tableau récapitulatif des espèces implantables au printemps et des délais de semis à respecter en fonction des spécialités herbicides employées en début de campagne.
Vos contacts régionaux
- Quentin LAMBERT (q.lambert@terresinovia.fr) – Ingénieur régional de développement – Occitanie
- Quentin LEVEL (q.level@terresinovia.fr) – Ingénieur régional de développement – Ex-Aquitaine, Gers, Hautes-Pyrénées

Mastering camelina cultivation

Our other training courses
Camelina: transforming a diversification crop into a technical and economic opportunity.
Boosted by a rapidly expanding market, camelina requires precise control of its cultivation itinerary if it is to achieve its full potential. This training course offers a complete technical and economic approach to successfully integrating camelina into cropping systems.
The program includes
1. camelina: basics and challenges
- Origin, development cycle and agronomic characteristics
- Crop strengths and positioning in cropping systems
2. market opportunities and value-adding framework
- Main outlets: sustainable fuels, food and feed, cosmetics, industrial uses
- Regulatory context
3.camelina technical itineraries
- Conditions for success and choice of plot
- Planting and varietal selection
- Fertilization and weed management
- Pest and disease management
- Adapting the itinerary to the type of crop: main crop, summer or winter catch crop, intercropping
4 Harvesting and securing production
- Key harvesting principles and settings
- Mowing and raking
5.camelina in organic farming
- Agronomic benefits
- Technical specificities and outlets
6.economic performance
- Comparison of margins according to technical itineraries
- Economic analysis at crop system level
7.field diagnosis
- Observation of plots and/or trials
- Collective analysis of situations encountered
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Understand the agronomic, economic and regulatory issues involved in growing camelina.
- Identify the various outlets for camelina and their requirements
- Recommend key cultivation techniques for successful camelina production, whatever the cropping method (main crop, catch crop, combination, organic farming).
- Adapt camelina technical itineraries to soil and climate conditions and to production objectives.
Face-to-face format with a field component (depending on conditions and training period):
-
Theoretical classroom input: Presentation of the crop, its outlets and technical itineraries (main crop, catch crop, combination), illustrated by trial results and concrete case studies.
-
Field observation: Analysis of real-life situations in plots and observation of trials to carry out collective diagnoses and illustrate technical levers.
Active methods: Presentations, case studies, practical exchanges, questions and answers, applied diagnostics.
Assessment: Quiz to validate knowledge acquired, questions and answers throughout the course, self-assessment by participants, individual satisfaction survey.
Theoretical support: Presentations, lectures, regulatory texts and summary documents given to participants.
Case studies: Real-life situations based on experimental results and feedback from the field, analyzed collectively.
Practical exchanges: Sharing of experiences between participants and trainers to enrich technical analysis and diagnoses.
Technicians, agricultural advisors, farmers, agents of structures working with camelina for biofuel production Q&A, quiz, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioningIf you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the Disability Advisor:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 0€ TTC https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/h17x4yzwmvzfgytkjb6Aq7zA3flf2q6khf1xmsczn8qAw8jpnz5sw4brlfk2kAbynAvwgpj5h35tqtkdkrhg3rtsm7yAyrjA4rzs9vlhjr7g4pj8 1 Jour 102 Intra-entrepriseAgronomic control of chickpea and lentil cultivation in the southwest of France
Our other training courses
Integrating lentils and chickpeas into your crop rotations: a strategic agronomic choice
Lentils and chickpeas are economical, high-performance crops that improve soil fertility, break pest and disease cycles and offer secure outlets. Adapted to the pedoclimatic context of the South-West of France, the training course offers theoretical contributions and visits to master technical itineraries and integrate these legumes sustainably.
Program:
1 Introduction to legumes:
- Definition of legumes and how they work,
- Role of legumes in soil fertilization and crop rotation.
2 - Lentil management in the South-West of France
- Agronomic characteristics: spring species, low-input crop
- Typologies (blond, coral, green) and value-adding opportunities
- Adapting the technical itinerary to regional constraints: soil types, water availability, temperatures, etc.
- Planting, varietal selection, cultural management, fertilization, protection
- Harvesting: optimal conditions, equipment settings
3. chickpea management in the South-West
- Agronomic, environmental and economic benefits
- Regionalized technical itinerary: choice of sowing dates, densities, management in dry conditions, harvesting, storage and contracting.
- Management of pests and diseases specific to the region
4 Focus on organic farming
Training carried out in collaboration with FILEG (free for their members)
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Explain the agronomic functioning of lentil and chickpea crops
- Identify their agronomic, economic and environmental benefits
- Choose species and varieties suited to the soil and climate conditions of the South West of France
- Implement rational crop management: planting, fertilization, weed and pest management
- Diagnose the main crop accidents
- Apply good harvesting and post-harvest practices
- Integrate the specificities of organic farming into the local context
Face-to-face format:
-
In-class technical input: presentations, case studies, interactive discussions
-
Practical application in the field: plot visits, crop observation, etc.
Active methods: Illustrated presentations, debates, questions and answers, feedback
Evaluation: Quizzes, questions and answers, application exercises, individual satisfaction surveys, self-assessment
Theoretical support: Lectures, visual presentations, written material given to participants.
Field visits: Analysis of lentil and chickpea crops in real-life conditions, identification of key technical points.
Practical exchanges: Feedback from field experience and group discussions with the trainer.
Advisors/Technicians from development, economic and agri-supply organizations. Teachers. Farmers Quiz, Q&A, application exercise, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioningIf you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 480€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/nf6fsAsf4852qmjwlj3gqzsjgv6g97l3mn2x4ml2nbgwsAlx4flhkmk5mjww49tc3nbggpj5hjlw2765g8lhgyzA3fgAc9trjf8hmq5kmfbAcpj8 1 Jour Quentin LAMBERT 94 Inter-company and intra-companyGrowing soybeans successfully in the South-West
Our other training courses
Soya, a crop of the future to be mastered!
In a context of agro-ecological transition, soybeans are back in the spotlight thanks to their low input requirements and varied outlets. Boosted by regulatory and economic support (protein plan, MAEC, SIE...), this crop offers real opportunities in both conventional and organic farming. This training course will provide you with a comprehensive, practical technical approach to successfully manage each stage of the crop, secure your yields and make the most of your production.
The program includes
1 Plant and canopy functioning:
- Key aspects of soybean physiology and phenology
- Highlighting levers for improving yields
2 - Cultural management adapted to the South-West :
- Planting
- Weed management
- Crop protection
- Water management
- Harvest control
3 Diagnosis of major accidents :
- Recognition of soybean pests
- Identification of root and leaf diseases
- Frequent climatic accidents in the South West
4 Approach to organic crop management
5 - Soybeans in catch crops: some indicators
Training organized in collaboration with FILEG (free for their members)
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Understand how plants function
- Analyze the factors influencing yield and the technical levers for optimization
- Recommend key cultivation techniques for successful soybean cultivation
- Implement good harvesting practices
- Detect and diagnose major crop failures (pests, diseases, abiotic stresses)
- Adapt crop management to the specificities of organic agriculture
Face-to-face format (1 day) :
-
Theoretical input via illustrated presentations and case studies.
-
Interactive exchanges between participants and trainers to share experiences and questions.
Active methods: Presentations, case studies, debates, questions and answers.
Evaluation: Quiz, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.
Theoretical support: Lectures, presentations, written material given to participants.
Case studies: Feedback from the field to illustrate best practices and solutions.
Exchange of practices: Discussions and sharing between trainees and trainers.
Agricultural technicians and advisors, Farmers and producers, Agricultural teachers and trainers, Agronomic and technical sales managers in agricultural distribution, Agri-food / processing industry players Quiz, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioning.If you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 480€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/jv72wsdgmr5hgzdf4ztwyrdxmngvm7dw4brh16cxj27A2wrr38rcwz53hbfgy5lmmzt25pj5hj6x1Azrj77v46cnn83w99jvgngs98bvgzhfcpj8 1 Jour Quentin LAMBERT 93 Inter-company and intra-companyHemp: a high-potential crop that requires careful management
Our other training courses
A no-input crop requiring limited fertilization, hemp responds particularly well to the mastery of basic production techniques. The expansion of outlets (construction, automotive, textiles, human food) makes hemp a crop with interesting development potential. In terms of surface area, France is currently the world's 2nd largest producer.
Program:
- Presentation of the hemp industry: history, players and organization of the sector
- Hemp outlets: Main value-added sectors (textiles, construction, food, etc.)
- Hemp physiology: Understanding the key biological elements for optimized cultivation, and adaptability to climate change.
- Specificities of hemp cultivation: Adaptation to soils, choice of varieties, water and nutrient requirements.
- Harvesting techniques: methods and equipment for efficient hemp harvesting
- Identifying the main phytosanitary problems: Damage observed on the crop and prevention strategies
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Explain the organization of the hemp industry and its various stages of development
- Analyze the agronomic, economic and environmental issues involved in growing hemp
- Identify and recommend the key cultivation techniques for successful hemp cultivation for different outlets.
Theoretical presentations in the classroom: clear, concise presentations on the hemp industry, its challenges, cultivation techniques and outlets.
Discussions and debates: time for interaction between participants and the trainer to share experiences, ask questions and explore key points in greater depth.
Plot visits: hands-on observation of cultivation techniques, varieties, development stages and any phytosanitary problems.
Interactive approach: the trainer, hemp expert Louis Marie ALLARD, leads the session in a dynamic way, drawing on feedback and case studies.
Evaluation: End-of-session quiz, questions and answers, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.
Visual aids: illustrated presentations (diagrams, photos, graphs) to facilitate understanding of technical and economic concepts.
Pedagogical documents: handing out synthetic aids (data sheets, guides, memos) to enable participants to keep a written record of key information.
Knowledge acquisition tests: quizzes or questions and answers to assess participants' understanding and reinforce important points.
Plot visits: direct observation of crops, soils, varieties and cultivation practices, for hands-on immersion.
Development technicians, agri-supply and distribution professionals, teachers, farmers. End-of-session quiz, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioningIf you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 240€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/nntw98djkrbAcrl5pjxw46kbmfywgsk4mzsdmzlr3qzxcq5d475hm9brkjh279tymzkAspj5hj3v3slvknA2c9rw3zlv3yjtn3xAcmkAkf5h4pj8 1 Jour Louis-Marie ALLARD 50 Inter-company and intra-companyMastering sunflower cultivation
Our other training courses
A sustainable, competitive crop that provides ecosystem benefits, sunflower needs to be managed carefully to achieve its full potential. This training course provides you with the technical keys and agronomic benchmarks you need to secure your itineraries and maximize field performance.
Program:
- Plant physiology: the key stages in sunflower development, and the main abiotic factors influencing yield.
- Crop management: intercropping, planting, fertilization, weed control (including post-emergence), plant protection, irrigation, harvesting
- Analysis and management of crop accidents: identification, causes, means of action
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- recommend the key cultivation techniques for a successful technical itinerary in sunflower
- diagnose major accidents that may occur during the crop cycle
Hybrid format:
-
Remote theory (2 hours): Technical inputs, case studies, interactive quizzes via Teams.
-
Field practice (1 day): Analysis of plots, observation of development stages, diagnosis of crop accidents, exchanges with the trainer.
Active methods: Presentations, discussions, debates, questions and answers, case studies, field diagnostics.
Evaluation: Quiz, oral questions and answers, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment at start and end of training.
Theoretical support: Lectures, presentations, written material given to participants.
Management tools: Presentation of technical levers for adapting cropping itineraries to specific contexts.
Field visits: Observation and diagnosis in the field to analyze development stages and crop accidents.
Practical exchanges: Feedback, discussions and debates between participants and trainer to enhance learning.
Technicians from development, agri-supply and distribution organizations. Farmers. Teachers. Quizzes, oral questions and answers, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment at the beginning and end of the courseIf you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 700€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/jzldgwbA4zzf2qkx3v7t2ztqk8qA3Akqmjcdcyl44y7Am6syljsgyAjwjj5vsqldfn5vkpj5hjtgq9trgjjt2wcllfvtqr5qpjcvmAdmkn5h4pj8 2 Jours 49 Inter-company and intra-companyMaster the cultivation of lentils, an interesting diversification crop for your rotations!
Our other training courses
A spring crop with many advantages, lentils lengthen rotations, break the cycle of pests and diseases, and require no nitrogen, making them particularly well-suited to the current context. Although lentils are often compared with faba beans and protein peas, they have their own specific technical itinerary, which needs to be mastered to guarantee satisfactory yields. This training course will help you to grow it successfully, whether organically or conventionally, by making the right technical choices.
Program:
- International and national context
- Lentil physiology and phenology: fundamental principles and key aspects
- Cultural management and associated decision-making rules (planting, varietal choice, crop associations, weed management)
- Harvesting techniques adapted to lentils
- Identification and management of the main damage observed on the crop
- Specific features of lentil production in organic farming
- Plot visits and practical crop analysis
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Understand the international and national production context, as well as the major challenges facing the industry.
- Identify the strengths and weaknesses of the species
- Design and implement appropriate crop management: previous crops, planting, choice of inputs, etc.
- Implement and/or recommend key cultivation techniques for successful lentil cultivation in organic and conventional farming.
- Diagnose the main accidents observed in cultivation
- Define good harvesting practices
Hybrid format:
-
Theory in the classroom: Technical inputs on crop management, discussions and debates.
-
Field practice: Plot visits, observation of development stages, crop analysis in real-life conditions.
Active methods: Presentations, case studies, questions and answers, sharing of experiences between participants and trainer.
Evaluation: Quizzes, oral exchanges, individual satisfaction surveys, self-assessment.
Theoretical support: Lectures, visual presentations, written material given to participants.
Field observation: Plot visits and observation under real conditions to link theory and practice.
Practical exchanges: Feedback from experience, discussions on concrete cases encountered in the field.
Technical tools: Presentation of useful references and documents for monitoring technical developments in cultivation.
Development technicians, agri-supply and distribution professionals, teachers, farmers. Quizzes, oral exchanges, individual satisfaction surveys, self-assessment.If you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 480€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/jnbw46rl4j1wqvjwpjgAmt63jzn2yws4pbj2ktdgn8n24663gj2g7wdsgnktqqlkjvkt3pj5h36tg6rxmy5Aymjt3ztgg75qmrbh25lwgfxvcpj8 1 Jour Zoé LE BIHAN 45 Inter-company and intra-companySoya: a strategic crop for sustainable systems
Our other training courses
Soya, a crop of the future to be mastered!
In a context of agro-ecological transition, soybeans are back in the spotlight thanks to their low input requirements and varied outlets. Boosted by regulatory and economic support (protein plan, MAEC, SIE...), this crop offers real opportunities in both conventional and organic farming. This training course will provide you with a comprehensive, practical technical approach to successfully manage each stage of the crop, secure your yields and make the most of your production.
The program includes
1 Plant and canopy functioning:
- Key aspects of soybean physiology and phenology
- Highlighting levers for improving yields
2 - Cultural management and associated decision-making rules:
- Planting
- Weed management
- Crop protection
- Water management
- Harvest control
3 Diagnosis of major accidents :
- Recognition of soybean pests
- Identification of root and leaf diseases
- Frequent climatic accidents
4 Approach to organic crop management
5 Soybeans in catch crops: a few indicators
At the end of the course, participants will be able to :
- Understand how plants function
- Analyze the factors influencing yield and the technical levers for optimization
- Recommend key cultivation techniques for successful soybean cultivation
- Implement good harvesting practices
- Detect and diagnose major crop failures (pests, diseases, abiotic stresses)
- Adapt crop management to the specificities of organic farming
Face-to-face format (1 day) :
-
Theoretical input via illustrated presentations and case studies.
-
Interactive exchanges between participants and trainers to share experiences and questions.
Active methods: Presentations, case studies, debates, questions and answers.
Evaluation: Quiz, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.
Theoretical support: Lectures, presentations, written material given to participants.
Case studies: Feedback from the field to illustrate best practices and solutions.
Exchange of practices: Discussions and sharing between trainees and trainers.
Agricultural technicians and advisors, Farmers and producers, Agricultural teachers and trainers, Agronomic and technical sales managers in agricultural distribution, Agri-food / processing industry players Quiz, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-positioning.If you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 480€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/hbjx4nt34fAg5zdd3vdfs5c3g2vA366pj1vv2vbpm8wx2t5xjbdvczkfgn5xc6dmnfsvcpj5hjgfmrdg3f6x3Ads4bngsk6hjy6fgmjwpfd2cpj8 1 Jour 44 Inter-company and intra-companyThe basics of rapeseed cultivation
Our other training courses
As rapeseed evolves, so does your knowledge!
With the rapid evolution of varieties, technical itineraries and decision-making tools, this training course offers a complete update on how to optimize rapeseed cultivation. Whether you're an experienced technician or a beginner, you'll discover the keys to success: genetic innovations, high-performance agronomic levers and benchmarks for making the right decisions at every stage of the campaign.
Day program :
- Yield development diagram and yield components
- Influence of different cultivation techniques
- Results of trials and surveys
- Main cropping decisions and decision rules
At the end of the course, participants will be able to:
- Identify rapeseed yield components and how they are determined
- Analyze the impact of cultivation practices on crop performance
- Select the varieties and inputs best suited to their soil and climate conditions and production objectives
- Adapt technical itineraries according to development stages and conditions encountered
- Make informed decisions throughout the growing season, based on technical, economic and agronomic data.
Active teaching methods: Technical presentations, case studies, feedback, alternating between theoretical input and feedback from field experience.
Evaluation: End-of-session quiz, questions and answers, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.
Theoretical support: Lectures, presentations, written material given to participants.
Exchange of practices: Feedback and debates between participants and trainers.
Interactivity: Quizzes, questions and answers, live exchanges with trainers.
Digital supports: Presentations and resources handed out after each session.
Technicians from development, economic organizations and the agri-supply industry. Teachers End-of-session quiz, Q&A, individual satisfaction survey, self-assessment.If you have any requests for adaptations to help you succeed in your course, please contact the disability referent:
Christel CARO
Tel: 01 30 79 95 09
Mail: formation@terresinovia.fr
Aucun 480€ TTC 5 15 https://public.dendreo.com/4rsx27tf4npws6tp4zAwc/media/gvhtcAdgnndxqAlgg8vAks6n3j6fg9tsj8vg4kzpmnxf4qk2gfhtmAsqkbyg5yzz4zcAspj5hjyAg9k5hbAg4sttlb3A4v544ncAwtcrljvAcpj8 1 Jour 40 Inter-company and intra-company